31+ Green Vegetables List (From a Nutritionist)
What are the health benefits of eating green vegetables and what are the best green vegetables? This article includes tips on how to incorporate these healthy foods into your daily diet. Enjoy this Green Vegetables List which includes both leafy and non-leafy greens.

While all vegetables are worth including in your diet, green vegetables have unique benefits.
Green Vegetables List (Summarized)
Here’s a list of green vegetables to help get you started. Scroll or click to get more information on each one, including some recipes and tips on preparation.
- Green squash
- Dandelion greens
- Microgreens
- Herbs
- Green beans
- Broccoli
- Watercress
- Cabbage
- Brussels sprouts
- Bok choy
- Kale
- Spinach
- Swiss chard
- Okra
- Asparagus
- Celery
- Cucumber
- Green peppers
- Tomatillos
- Arugula
- Collard greens
- Green onions
- Leeks
- Artichokes
- Fennel
- Endive
- Broccoli Rabe
- Peas
- Romaine
- Beet greens
- Mustard greens
Green Vegetables List (Expanded)
1. Green Squashes

Yes, squash can be green! Some varieties of green squash include zucchini, romanesco zucchini, cousa squash, pattypan squash, and chayote squash.
Green squash is healthy and contains chlorophyll and other antioxidants as well as Vitamin C. They’re also a good source of beta carotene, B vitamins, and fiber.
I find zucchini to be a particularly mild-tasting green vegetable. I like using it in my recipes for Instant Pot Zucchini and Tomatoes, Vegan Zucchini Brownies (you read that right!), or Air Fryer Zucchini Chips
2. Dandelion Greens

Dandelion greens are a type of wild lettuce that can be found growing in many parts of the world. They have a bitter taste and are high in vitamins and minerals.
Dandelion greens can be eaten raw or cooked, and are a popular ingredient in salads and soups. They are considered a leafy green vegetable.
I personally find them to be on the bitter side, so I most often blend them into a green smoothie. You may also like my article on the Health Benefits of Green Smoothies.
Dandelion greens are also on my list of the best gut healing foods!
3. Microgreens

Microgreens act as a fun garnish for salads, sandwiches, and many other dishes. In addition to being pretty, they are incredibly healthy.
They pack a nutrient punch in a smaller serving. They’re the immature, seedling form of bigger greens like radishes, cilantro, and broccoli and contain as many nutrients as their mature counterparts. These nutrients depend on the microgreen, but can include Vitamin C, chlorophyll, beta carotene, Vitamin K, B vitamins, and Vitamin E.
Learn how to grow broccoli sprouts right on your kitchen countertop. Then, learn how to eat broccoli sprouts and other microgreens, including broccoli microgreens, spinach microgreens, radish microgreens, or arugula microgreens.
See my list of the healthiest microgreens to eat.
4. Herbs
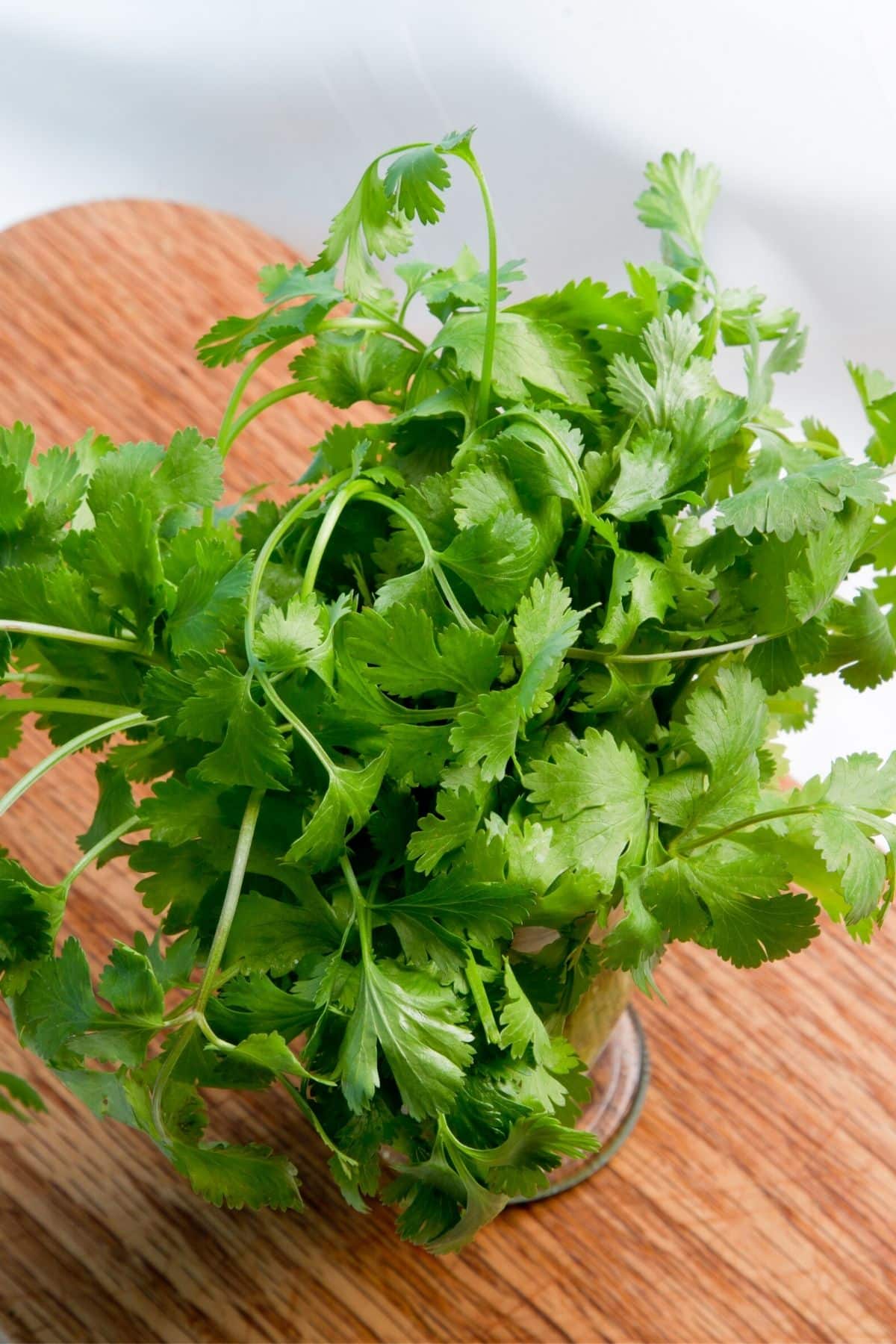

Don’t forget your herbs when considering green vegetables to add into your diet!
Dried or fresh, herbs are incredibly nutrient-dense green vegetables. Herbs like cilantro, basil, parsley, chives, rosemary, and others contain chlorophyll, antioxidants, beta carotene, Vitamin C, and even anti-fungal properties.
Cooking with herbs will give your dishes better flavor and more nutrients.
Some of my favorite recipes using herbs include my Green Vegetable Juice and my Parsley Juice. If you don’t want to make a juice with herbs, then simply start adding them to your meals as a garnish.
5. Green Beans
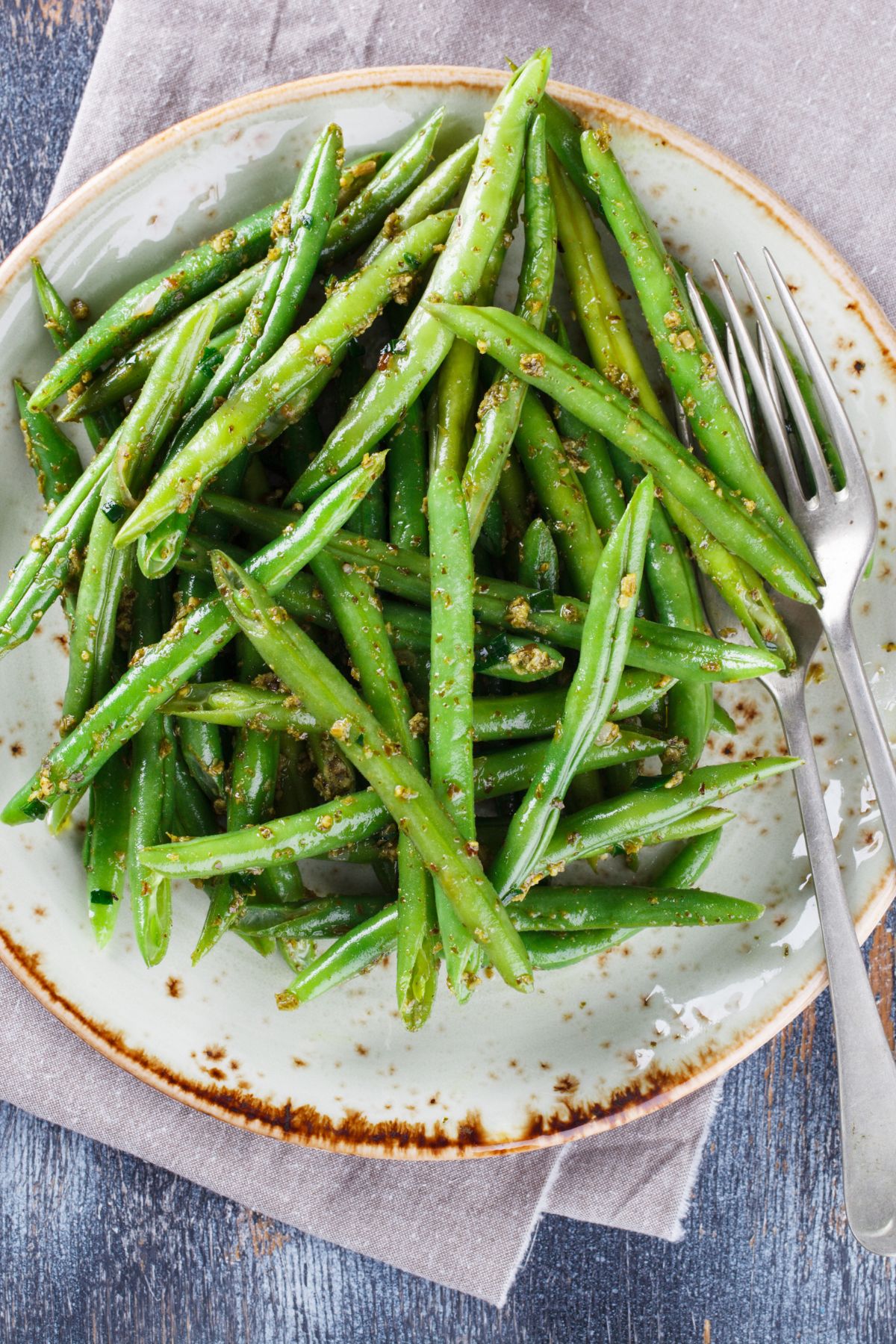

Green beans are a healthy type of vegetable that is long and thin with a green color. They can be eaten cooked or raw, and are a good source of dietary fiber, vitamin C, and vitamin K.
There are three main types of green beans: string beans, snap beans, and French beans. You can buy green beans fresh or frozen.
Some of my favorite recipes with green beans include Salmon Stir Fry, Air Fryer Green Beans and Air Fryer Frozen Green Beans.
6. Broccoli
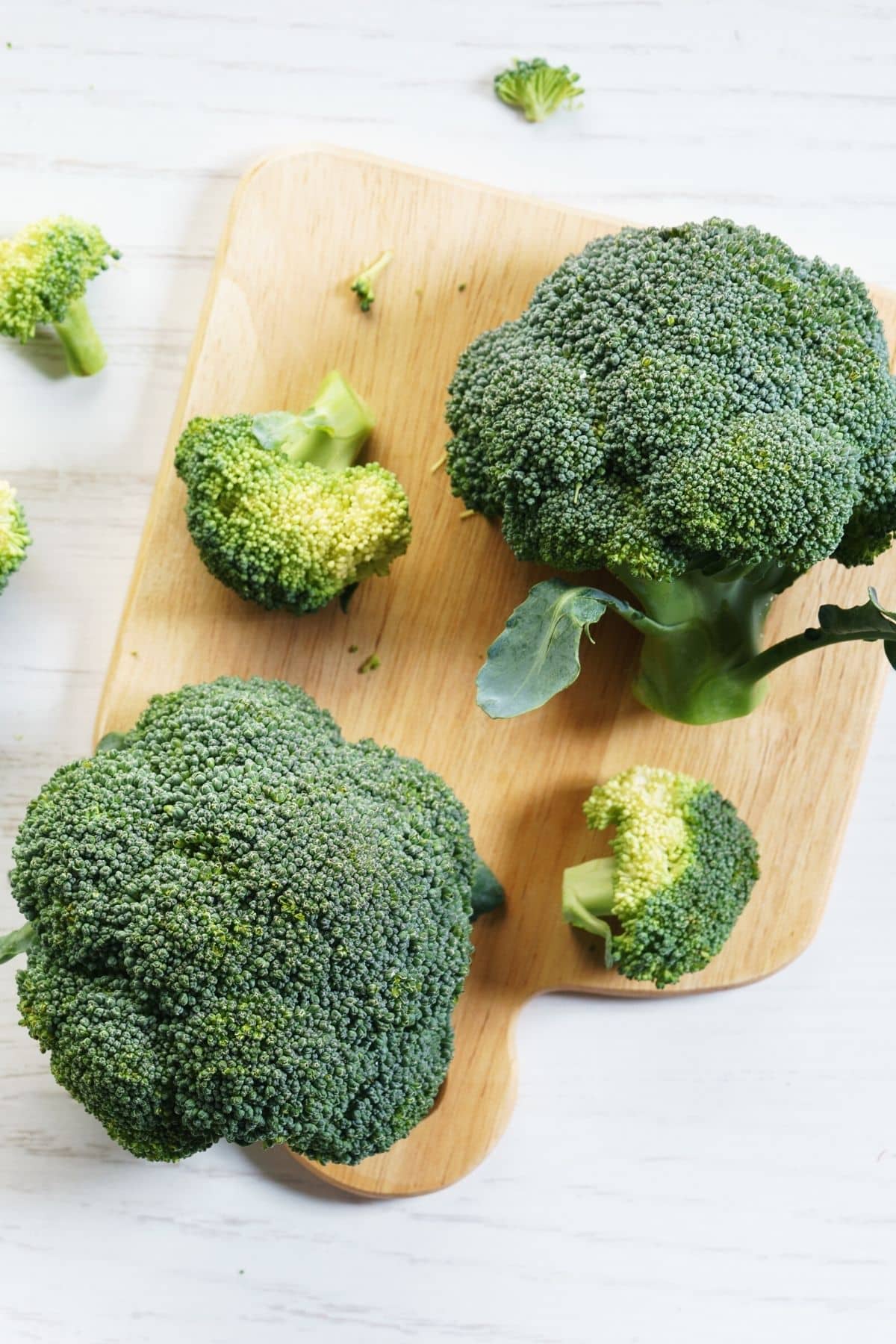

Broccoli florets are small, green florets that come off the main stem of the broccoli plant. They are usually cooked by boiling or steaming them, and they have a slightly bitter taste.
Broccoli florets are a good source of dietary fiber, vitamin C, and vitamin K. They are also a good source of cancer-fighting phytonutrients.
Eating broccoli may help protect against cancer, heart disease, and age-related macular degeneration. They are part of a family of green vegetables known as cruciferous vegetables.
Another nice things about broccoli is that it can grow most of the year so it’s easy to find in grocery stores, even in the wintertime. It’s usually not very expensive so it’s a very good value if you want to eat more vegetables. You can also find it frozen or canned.
I have lots of broccoli recipes on my site that taste good! If you think you don’t like broccoli, then try my Vegan Broccoli Potato Soup, Air Fryer Frozen Broccoli, or Roasted Frozen Broccoli. It’s also great to add in a stir-fry (see my Bison Broccoli Stir-Fry recipe).
7. Watercress
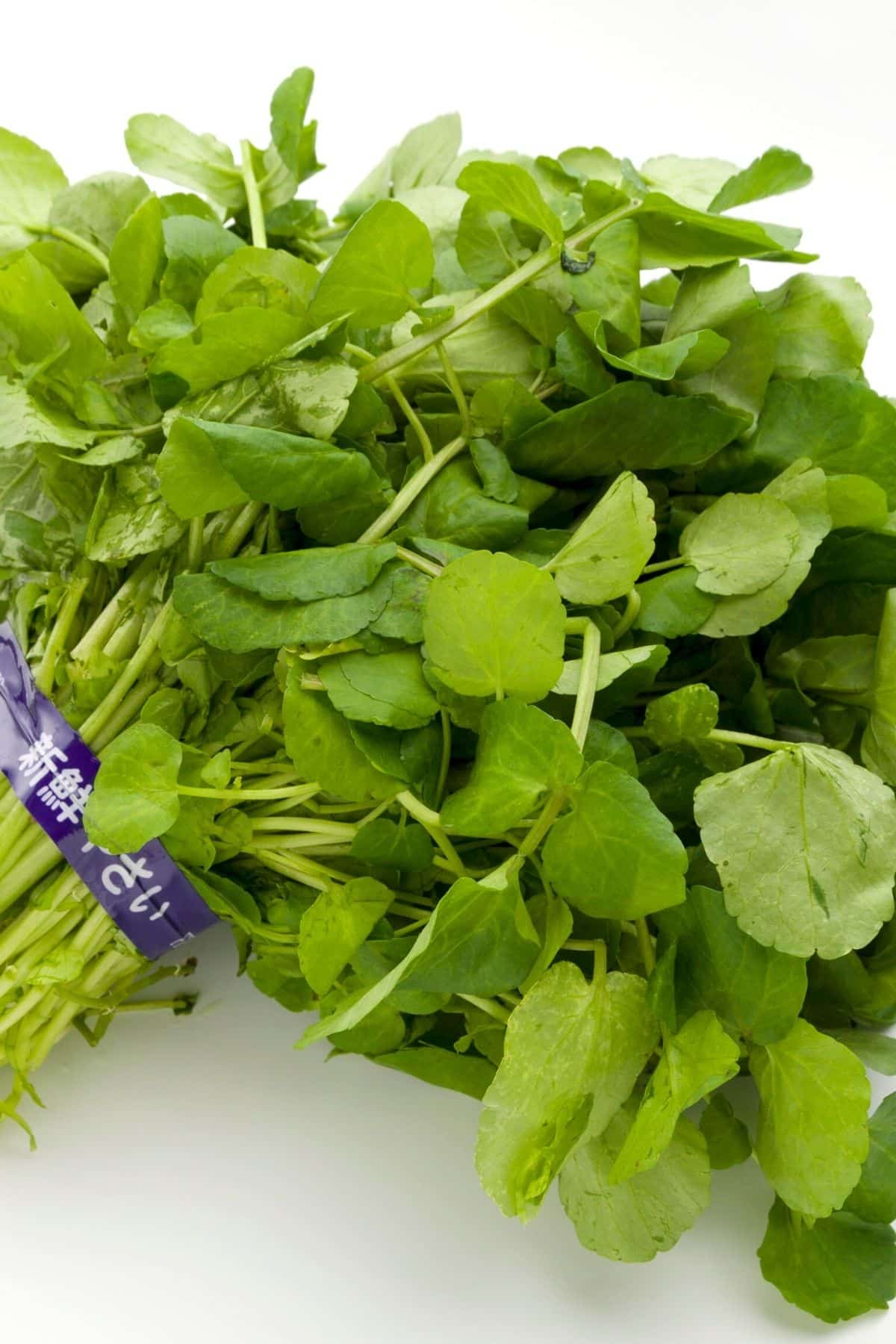

Watercress is a leafy green vegetable that is typically eaten raw. It has a peppery flavor and is high in Vitamin C and antioxidants. Some people think watercress is the most healthy green of all!
It is also a good source of calcium and iron. Watercress can be cooked in a variety of ways, including steaming, boiling, or sautéing. It is a healthy addition to any meal, but is most commonly served in a salad.
8. Cabbage
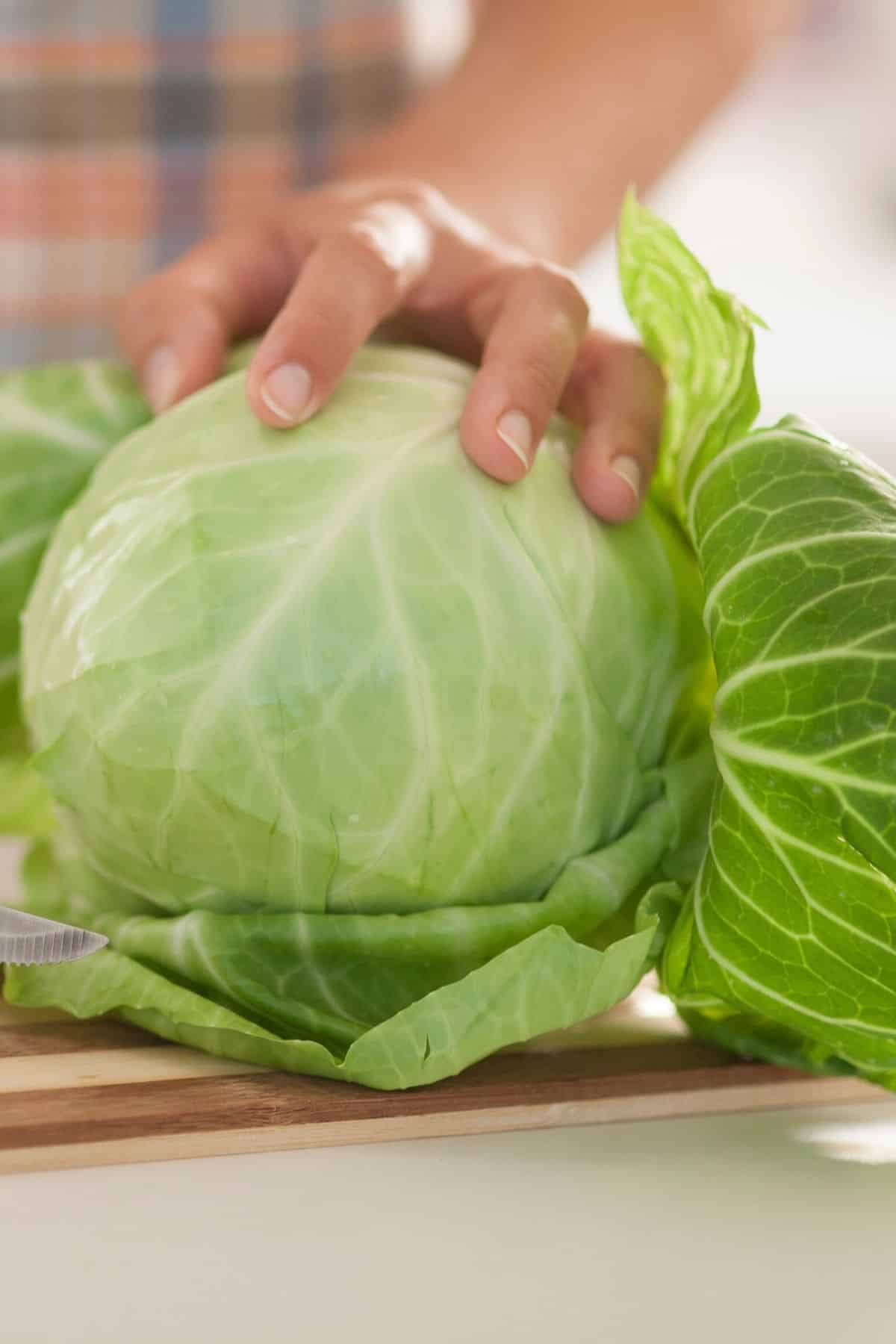

Cabbage is a nutritious vegetable that is often used in salads. It has a crunchy texture and a slightly sweet flavor.
Cabbage is a good source of fiber, vitamin C, and potassium. It is also a good source of antioxidants, which can help protect the body from disease.
Cabbages of all colors (red cabbage, green cabbage, purple cabbage) can be cooked in a variety of ways, including boiling, steaming, and frying. I have many cabbage recipes on my site including Cabbage Vegetable Soup, Slow Cooker Cabbage, and Instant Pot Cabbage.
Or, if you are feeling adventurous, try Cabbage Juice!
9. Brussels sprouts
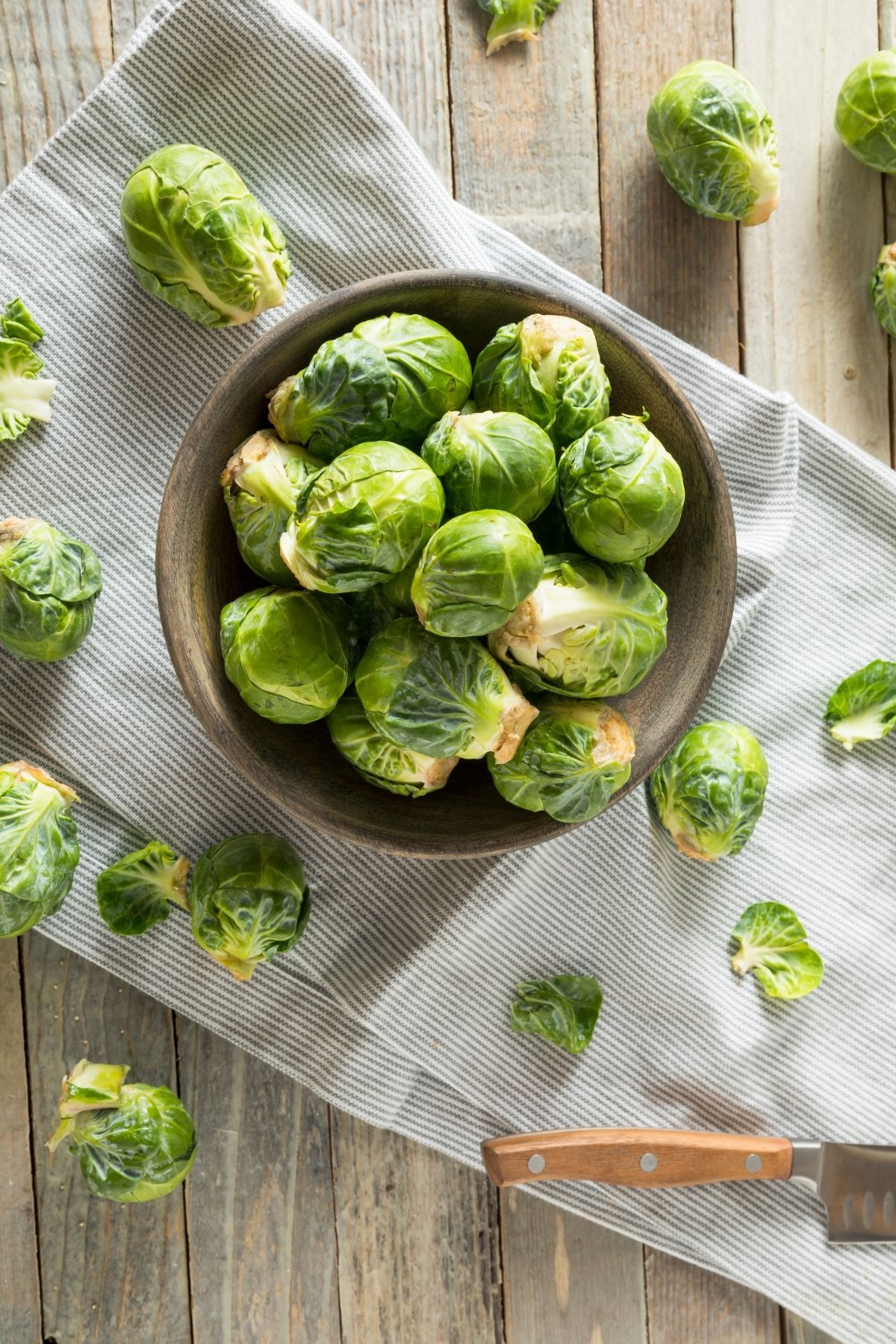

Brussel sprouts are a small, cabbage-like vegetable that is often boiled or roasted. They have a slightly bitter taste but are also somewhat sweet.
Note: some people refer to this baby cabbage veggie as a “brussel sprout”, but the correct term is Brussels sprout or Brussels sprouts.
Brussels sprouts are high in fiber and vitamin C, and they also contain antioxidants.
Here are some delicious Brussels sprouts recipes: Air Fryer Brussel Sprouts with Bacon and Frozen Brussel Sprouts in Air Fryer.
10. Bok choy
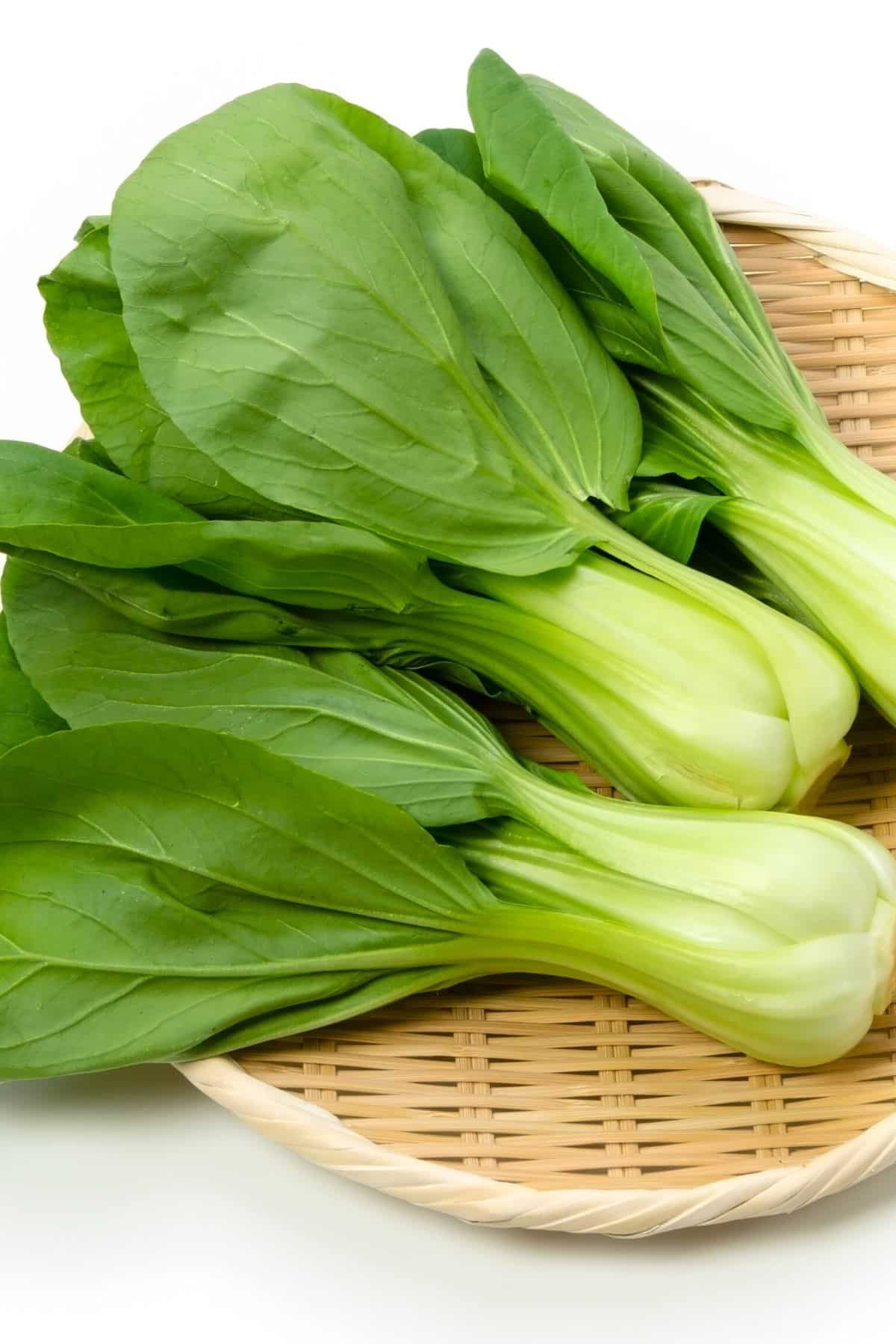

Bok choy is a type of healthy Chinese cabbage that has a white stalky center and green leaves. It has a mild, slightly sweet flavor and is a good source of fiber, vitamin C, and vitamin A.
Bok choy is a versatile vegetable that can be cooked in a variety of ways, such as steaming, stir-frying, or braising. I try to buy baby bok choy as opposed to the fully-mature bok choy as I think it is more tender.
11. Kale
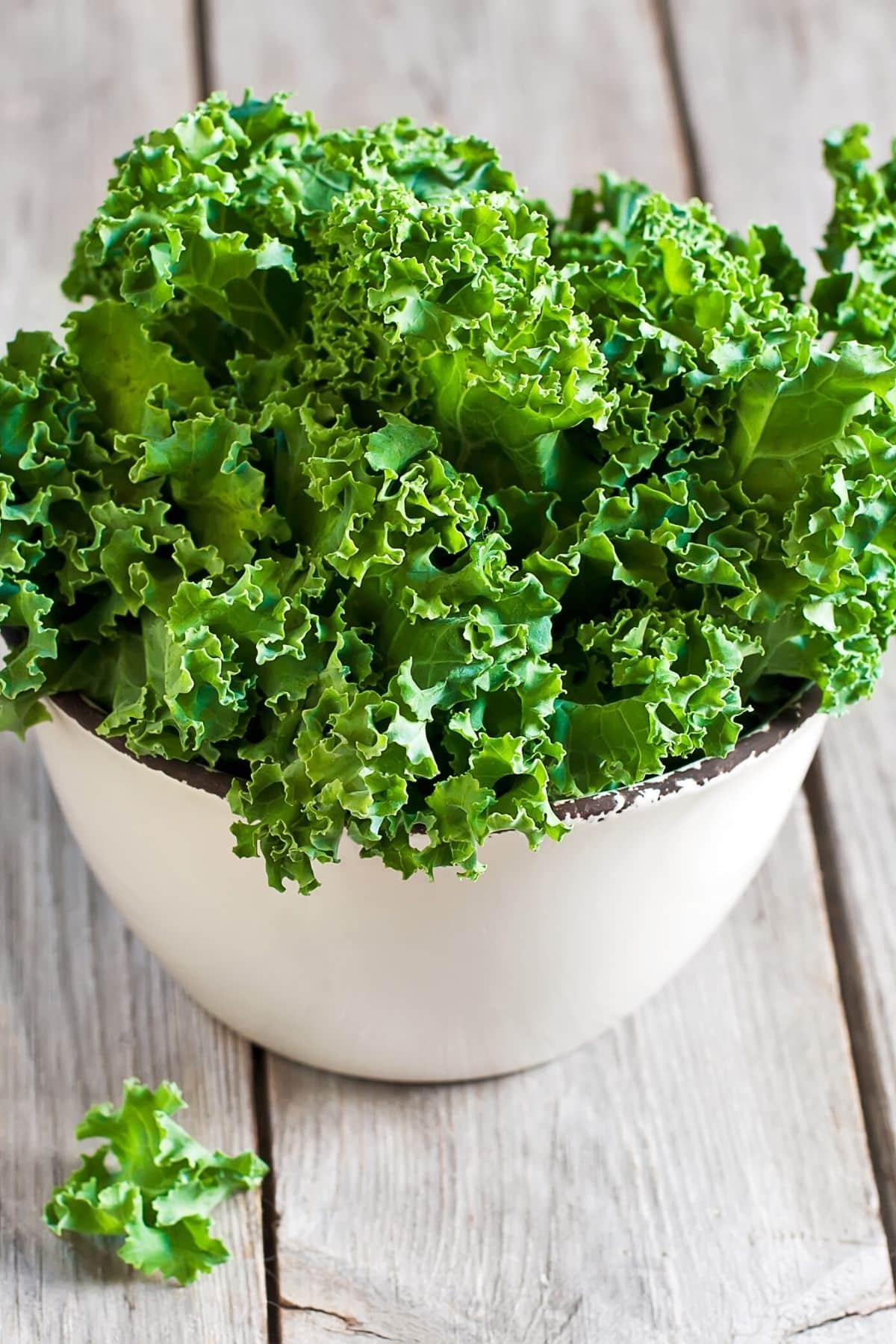

Kale is a dark, leafy green vegetable that is related to broccoli and cabbage. It has a slightly bitter taste and is a good source of Vitamins A, C, and K. Kale is also high in antioxidants and is considered a superfood.
It can be cooked in a variety of ways, including steaming, boiling, or sautéing. Kale is a healthy addition to any diet.
There are also different types of kale including Lacinato kale (on my list of the best vegetables starting with L), Tuscan kale, Dino kale, and more.
Some of my favorite recipes using kale include:
12. Spinach
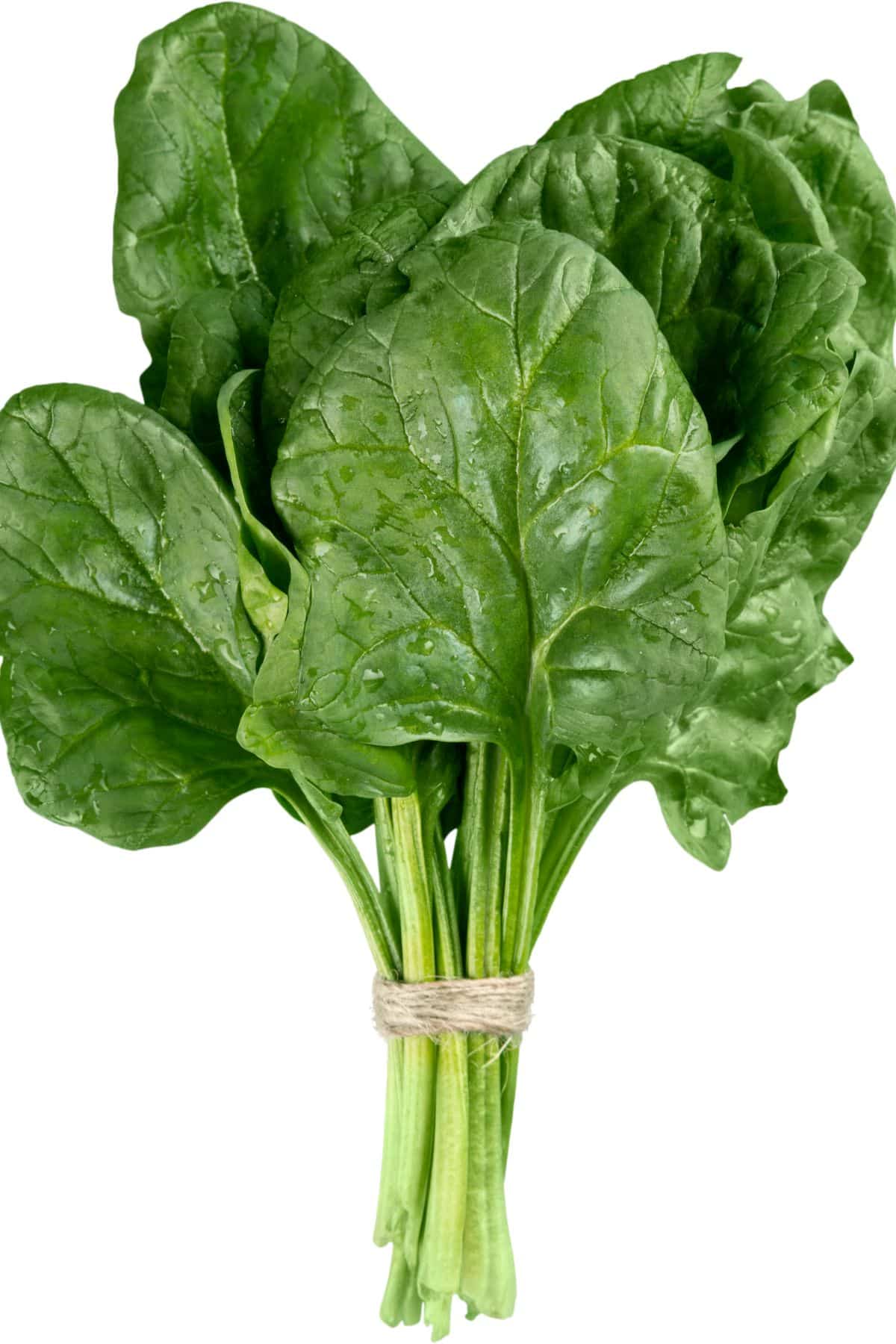

Spinach is a leafy green vegetable that has a mild flavor and slightly crunchy texture. It can be eaten raw or cooked, and is a good source of vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin K, magnesium, and folate.
Spinach can be eaten raw in salads or cooked in various dishes. It is best to cook spinach for a short amount of time, as overcooking can make it tough and bitter.
Baby spinach tends to be more tender than fully-grown spinach leaves.
Try spinach in these yummy recipes:
- Slow Cooker Chicken Stew with Lentils and Spinach
- Green Apple Smoothie with Spinach
- Food Processor Smoothie
- Spinach Juice
- Weight Loss Green Smoothie
Or, see my post on how to freeze spinach.
13. Swiss chard
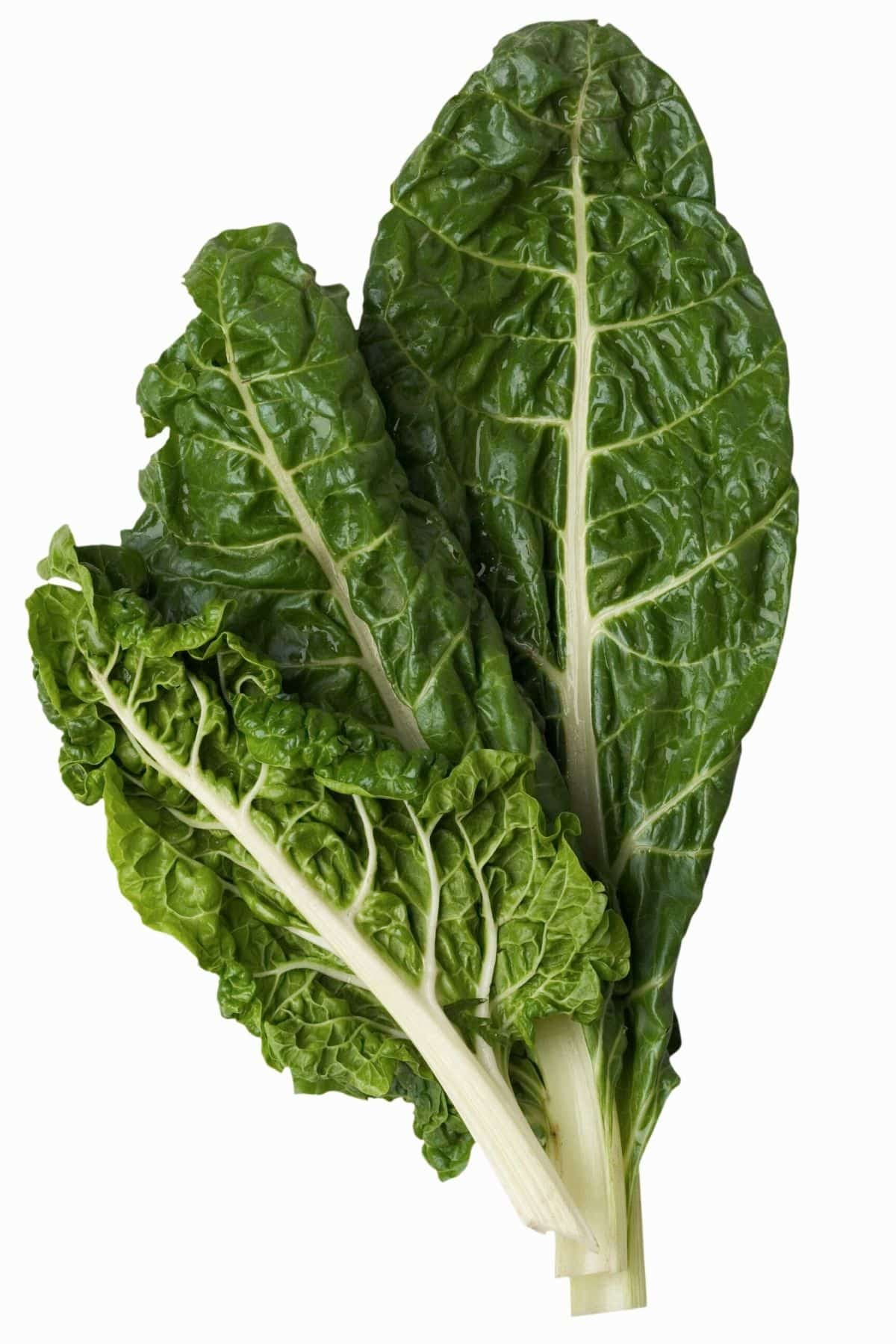

Swiss chard is a leafy green vegetable that is often used in salads or stir-fries. It has a slightly bitter taste and is a good source of vitamins A, C, and K.
Swiss chard also contains antioxidants and minerals such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium. Swiss chard is sometimes called Rainbow chard, and this is because you can find versions where the stems are colorful colors of red, orange, and yellow.
The stems are edible of both Swiss card and rainbow chard.
It can be cooked by boiling, stir-frying, or steaming. As noted, you can eat the stems of Swiss chard, in addition to the tender leaves. I love using it in my Swiss chard smoothie!
14. Okra
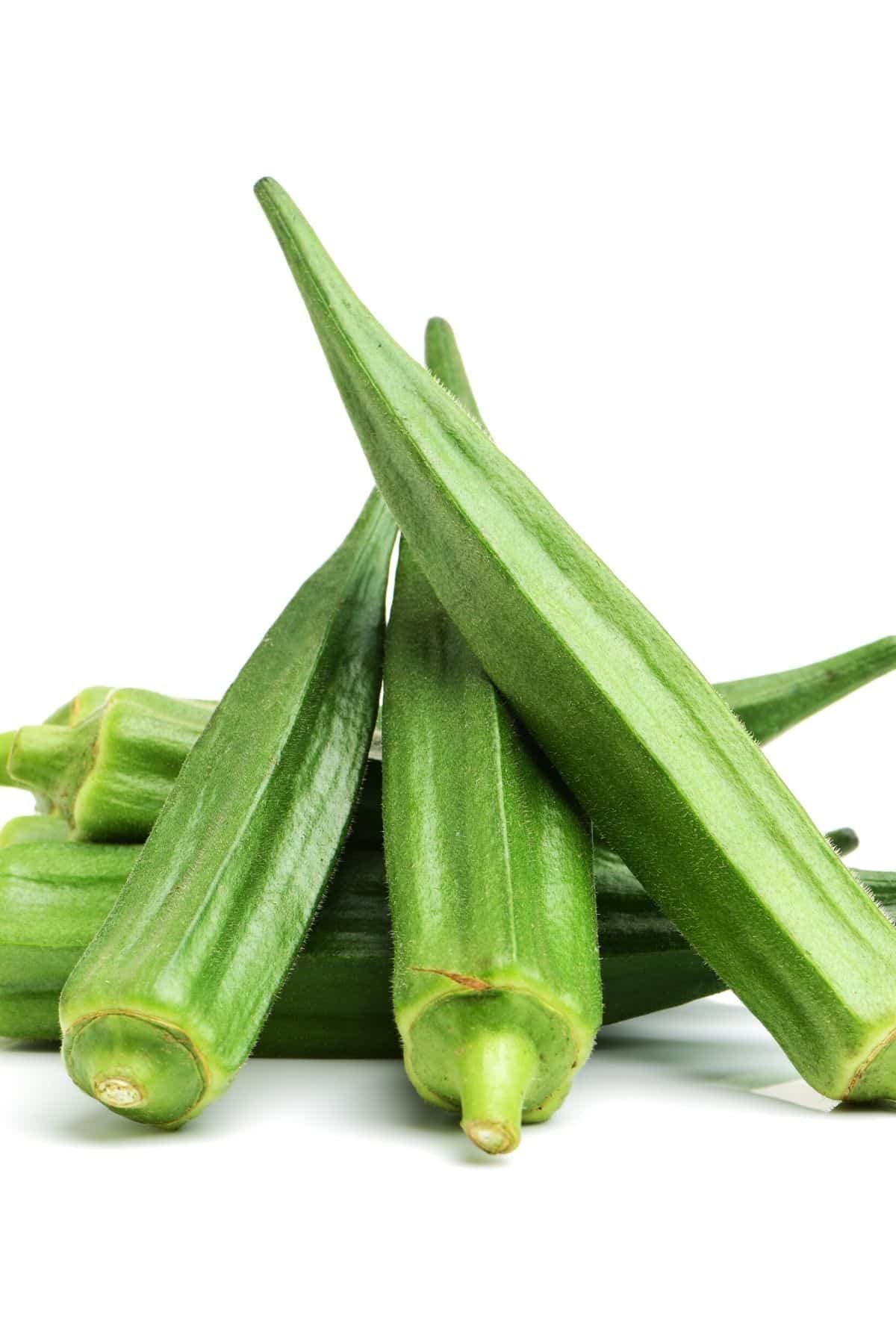

Okra pods are long and slender, and can be green, yellow, or red. They are usually about 6-8 inches long. The pods are edible, and the seeds inside are also edible.
It has a slimy texture and an unusual taste that takes some getting used to, but it is packed with nutritional value and can be cooked in a variety of ways.
In the United States, it is most commonly found in Creole cuisine, where it is often used in gumbo. I grew up in the Midwest where we ate a ton of okra pickles.
15. Asparagus
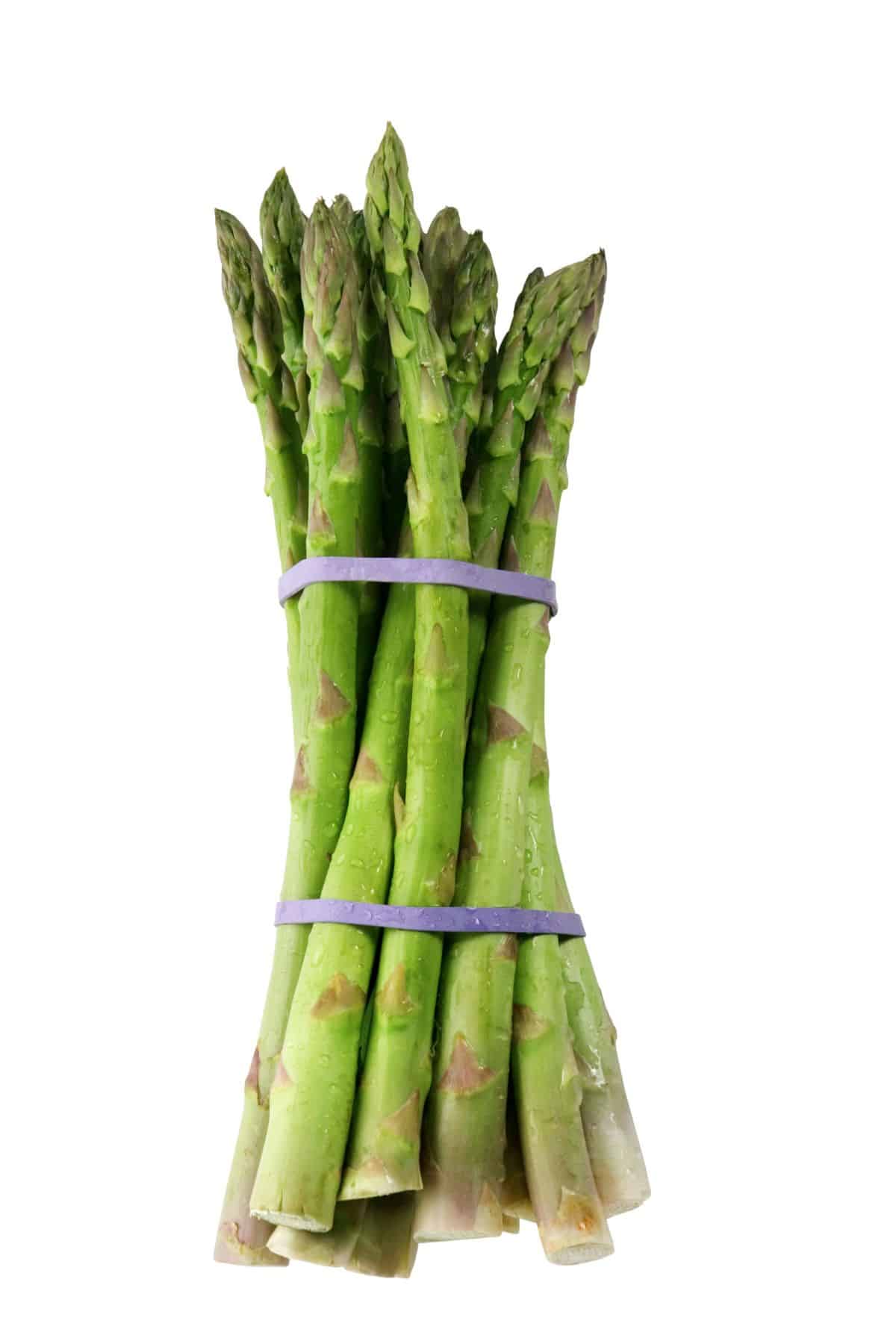

A vegetable that has been cultivated for as long as 2,000 years, asparagus is one of the oldest vegetables known to humans.
It can be found in many different areas around the world and comes in three colors: green, purple and white.
The tips are usually the most tender part of this vegetable while it’s stems are often tough and stringy. To prepare a dish with asparagus you must first snap off or cut off any woody parts at its base then boil or steam it until just cooked through.
Try my recipe for Instant Pot Asparagus.
16. Celery
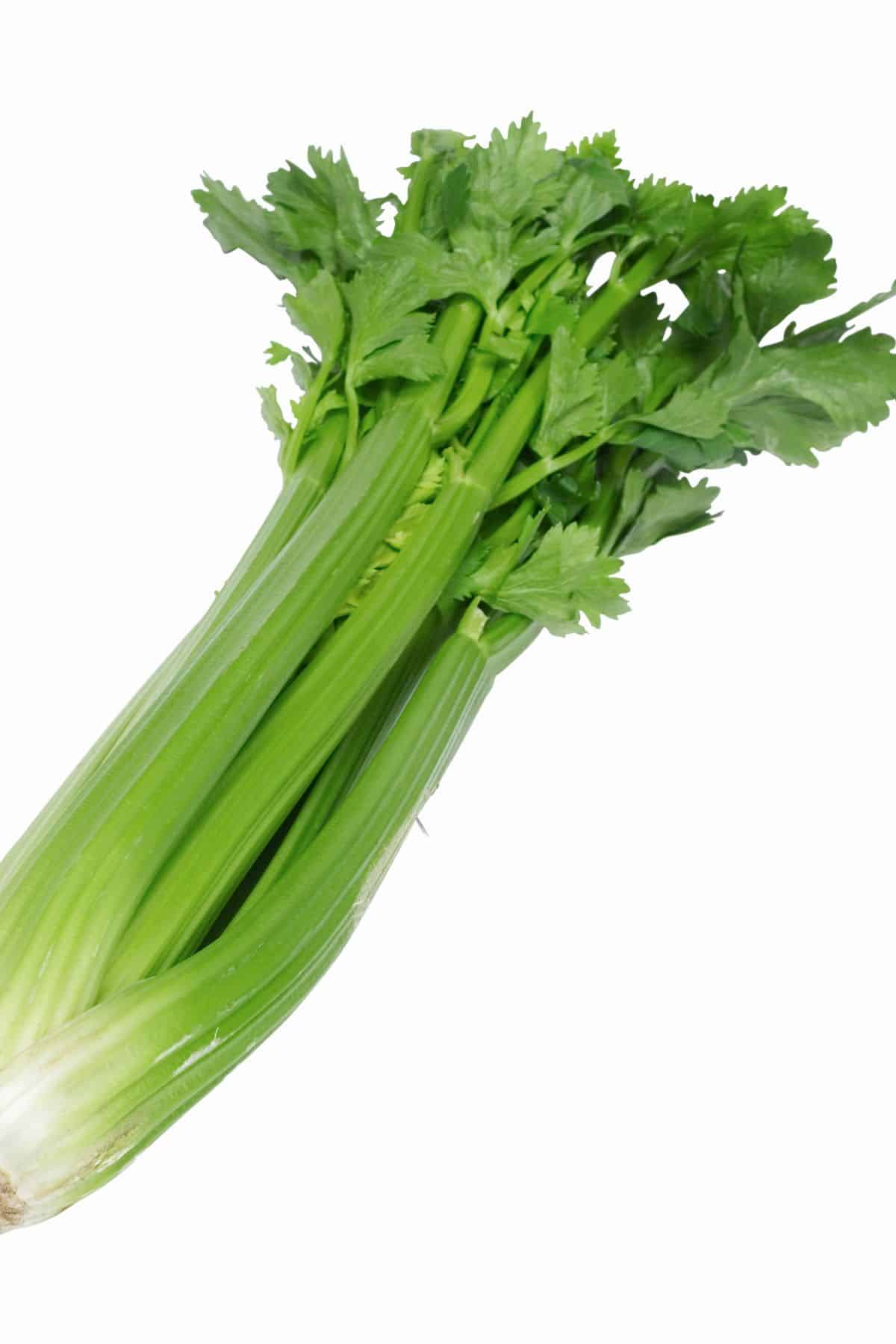

Celery is a crunchy vegetable that has a mild flavor. It is a great addition to salads or can be eaten as a snack. Celery is also high in fiber and vitamin C. It can be cooked by boiling, steaming, or microwaving.
But, celery in most often eaten raw in the United States. You can actually eat the leaves as well as the stalks, but it’s most common to just eat the washed celery ribs (also called celery stalks).
Celery is a great healthy snack and it’s also great for making Celery Juice! Or, try chopping it finely and adding it to tuna salad or almost any type of salad.
17. Cucumbers
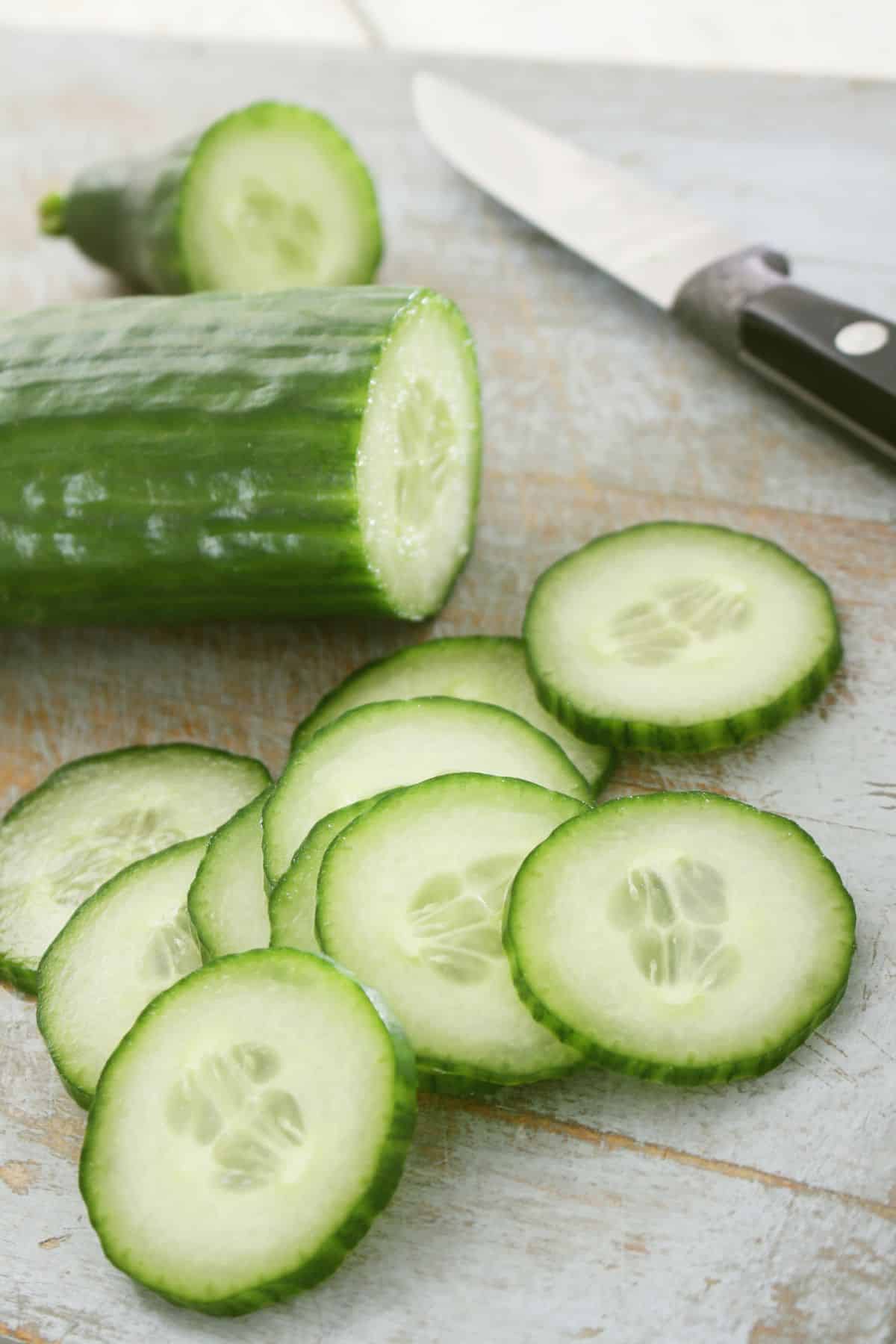

Cucumbers contain a lot of water. They’re cool, refreshing and thirst-quenching. In fact, the word “cucumber” comes from the Arabic word for cucumber, which is khiyar.
What’s great about cucumbers is that they can be used in both sweet and savory dishes! Not to mention that they are rich in vitamins A and C as well as potassium – so you know it’s good for your health too.
But how do you cook with cucumbers? Well there are a few ways: pickling them or adding them to salads, grilling or roasting them, or slicing thinly for sandwiches.
Don’t miss my recipes for Carrot Cucumber Salad, Cucumber Ginger Lemon Water, Cucumber Pico de Gallo, or Cucumber Juice.
Or, make a juice or smoothie using my list of Cucumber Drink recipes.
18. Green bell peppers
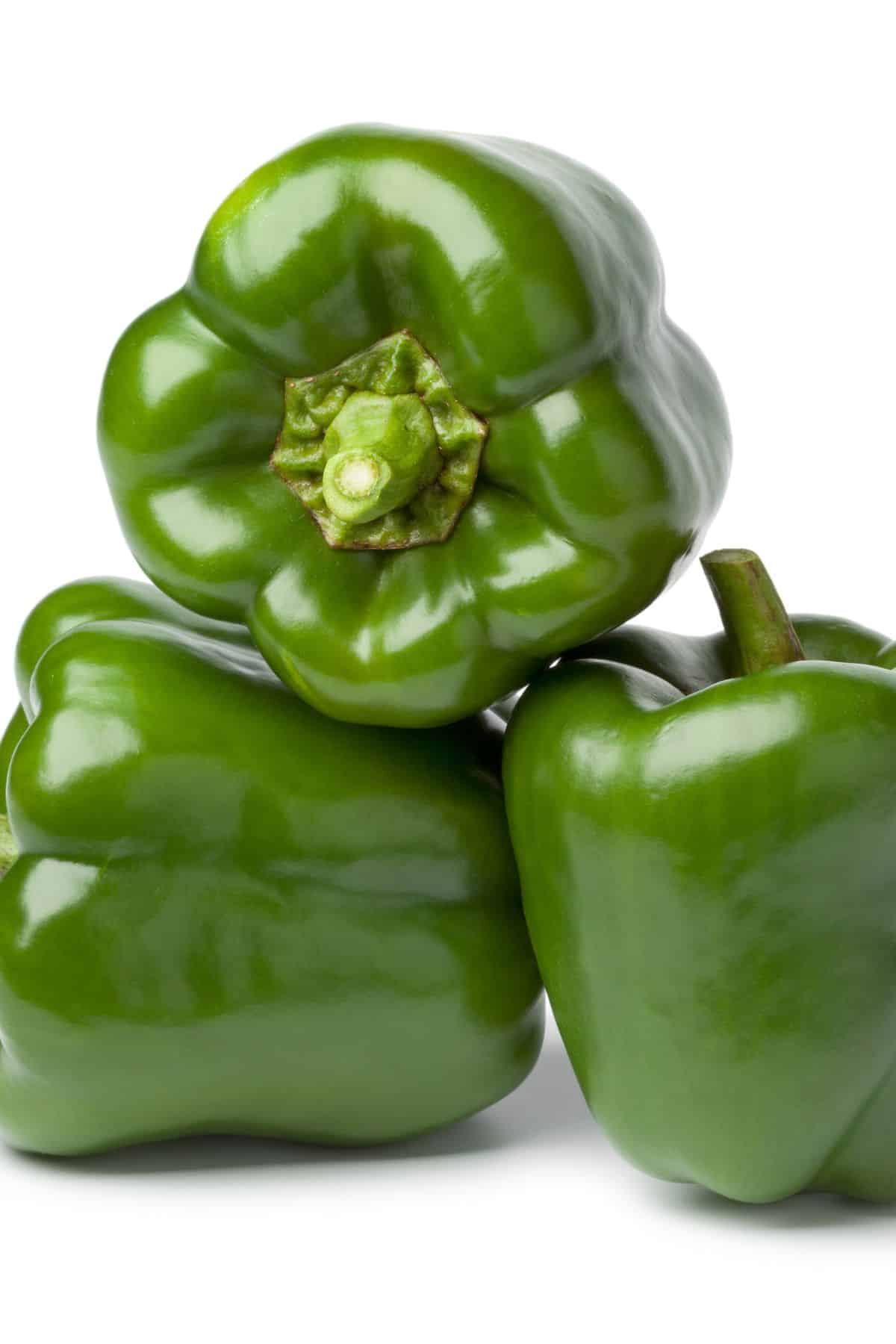

Most people know green peppers only as a crunchy addition to salads. But these versatile vegetables can be cooked in many different ways, and they have a unique flavor that makes them a great addition to many dishes.
Green peppers are bell peppers that have not yet turned red or yellow.
They typically have a slightly bitter taste, which some people like and others don’t. Green peppers are a good source of vitamin C, and they also contain antioxidants and other nutrients that are beneficial for your health.
Check out what to serve with stuffed peppers or how to freeze peppers.
19. Tomatillos
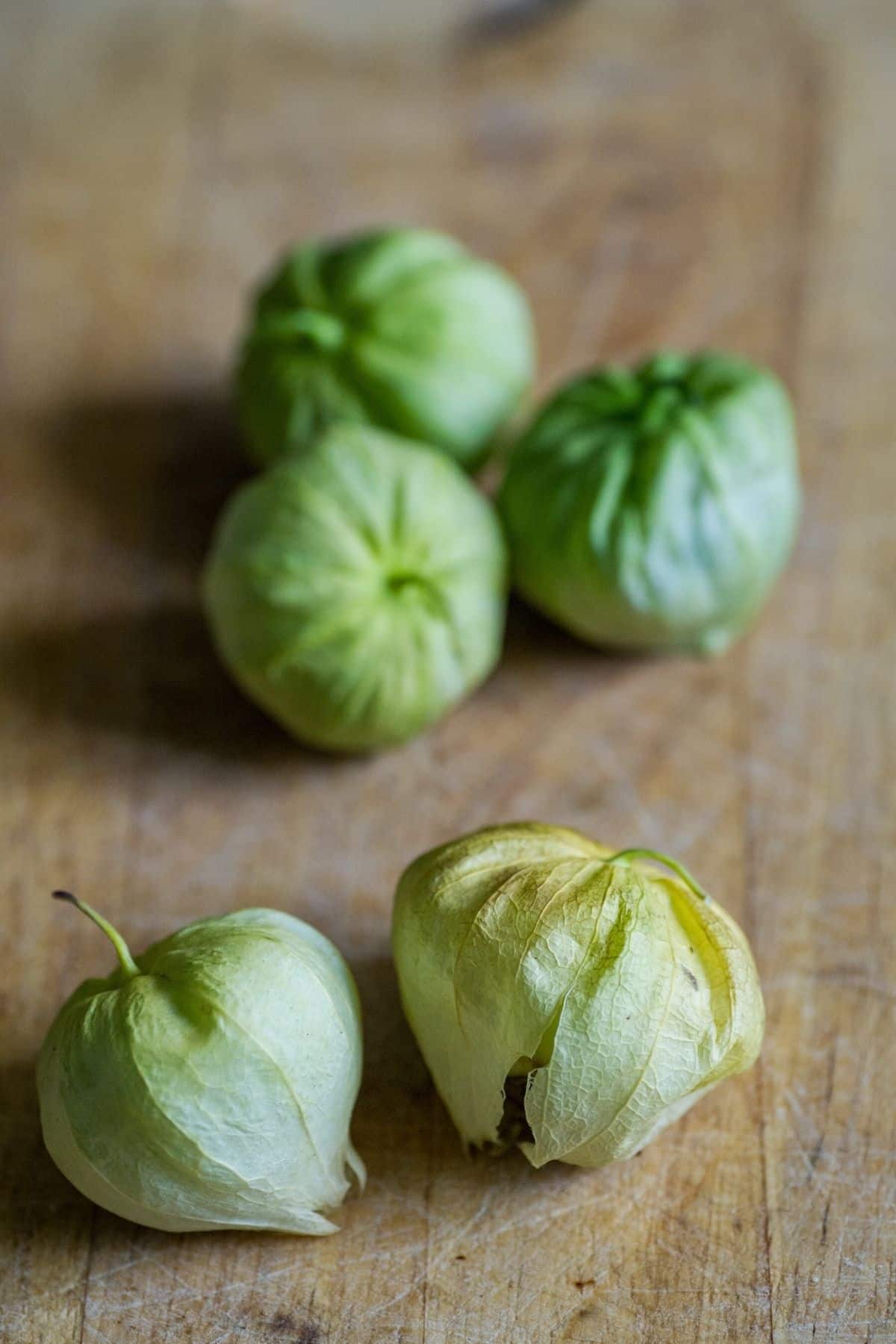

Tomatillos are a type of Mexican fruit that is green, tomato-like in texture and size, with a papery skin.
Though sometimes called “green tomatoes” or “Mexican tomatoes” to distinguish them from the red variety commonly found in supermarkets, tomatillos are not true tomatoes.
They grow on bushes as opposed to vine plants like regular tomatoes do.
Tomatillos have been cultivated by humans for centuries and were traditionally eaten raw as snacks or used in sauces and salsas because they taste much better when fresh than when cooked.
20. Arugula
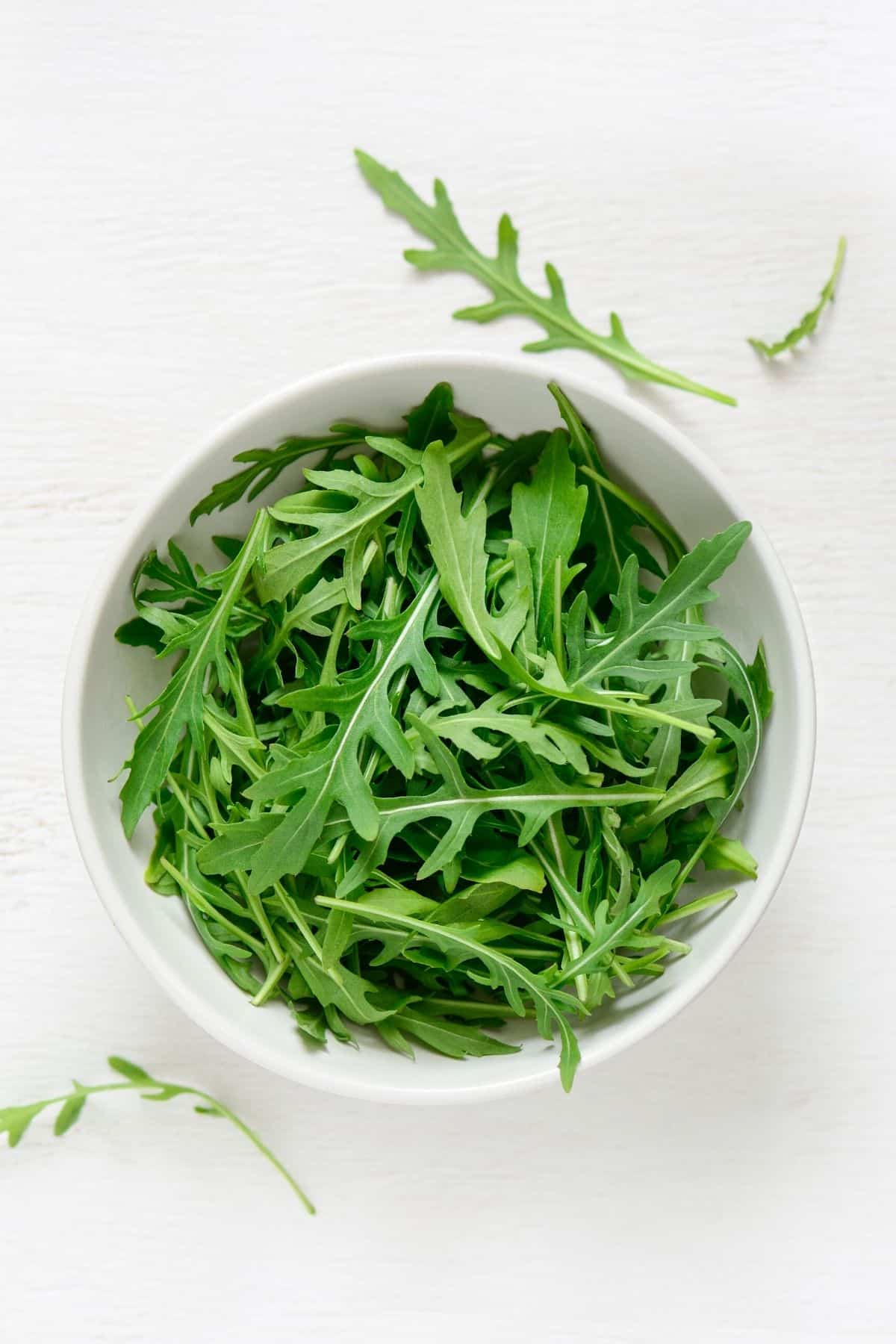

Arugula is a leafy green vegetable that has a peppery, slightly bitter taste.
It is typically used in salads, but can also be cooked. Arugula is high in Vitamins A and C, as well as folate. It also contains antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds.
21. Collard greens
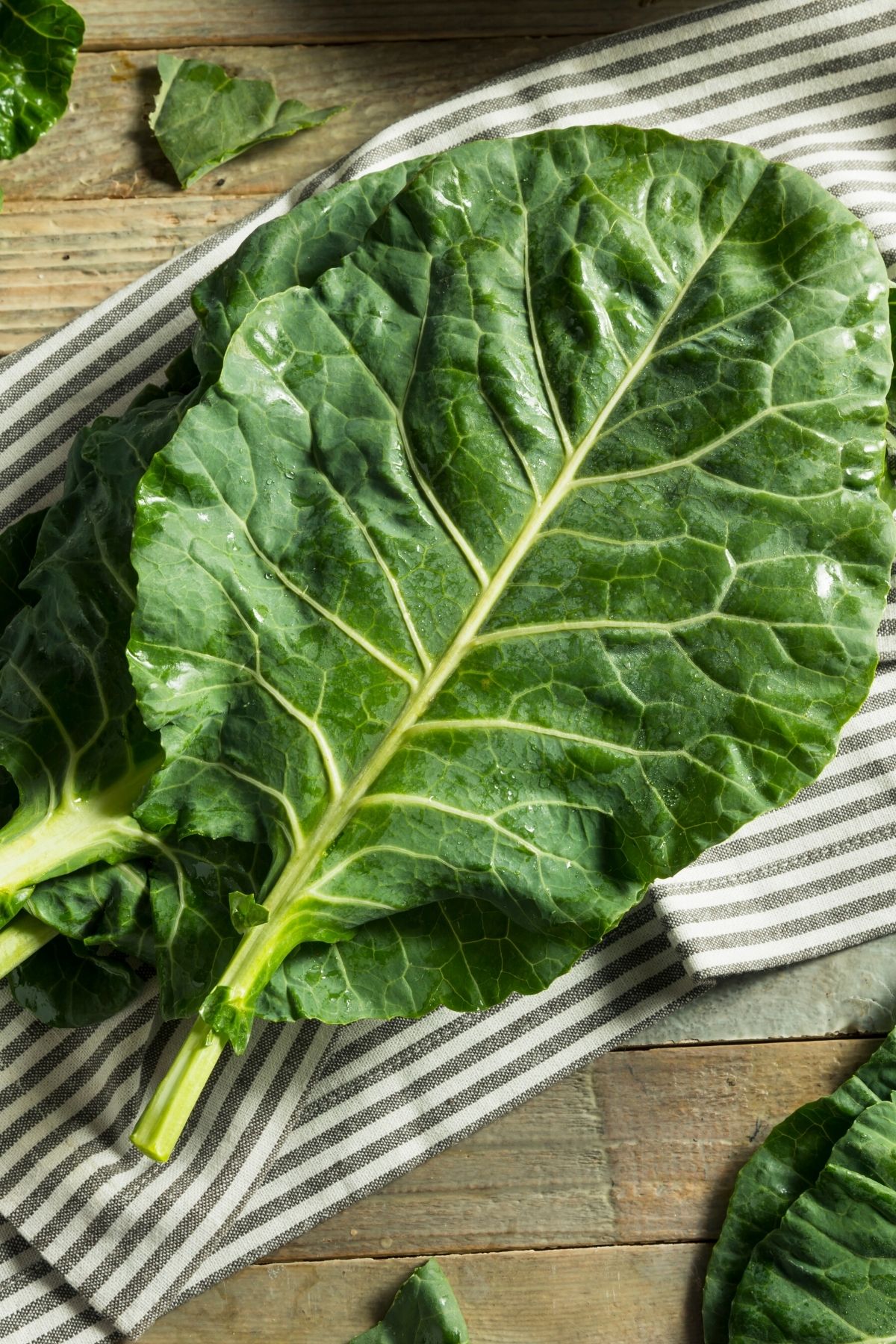

Collard greens have a thick stem and broad leaves and are related to broccoli, cabbage, and kale.. They can be green or purple in color.
Collard greens are usually cooked by boiling, braising, or steaming. They have a slightly bitter taste and are high in vitamins A, C, and K as well as minerals such as potassium and calcium.
In the United States, we often associate this vegetable with Southern cooking. I like to make a Collard Green Smoothie!
22. Green onions
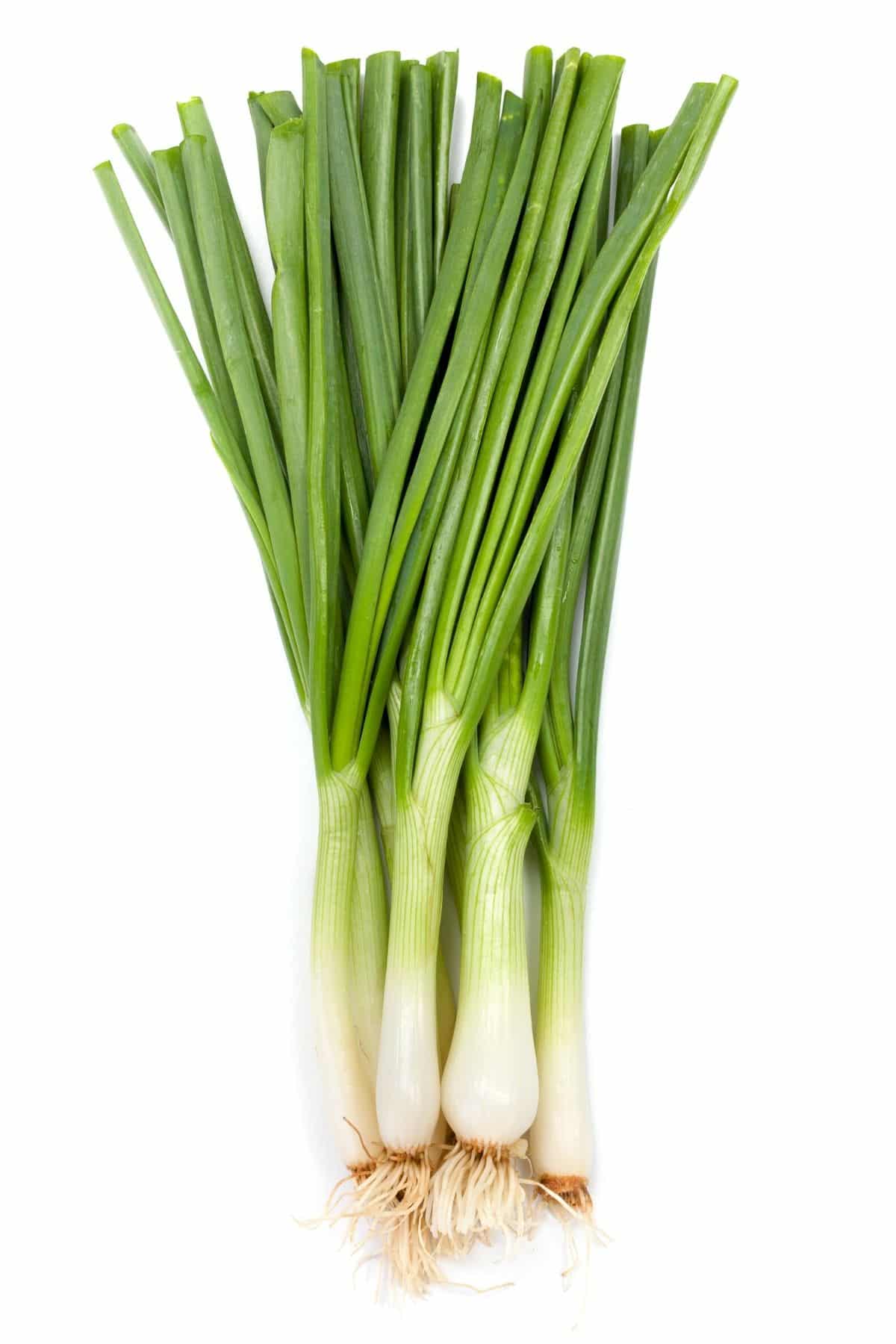

Green onions are a type of scallion that come in many varieties, the most common being a long green onion with white ends. They can be eaten raw or cooked and have a slightly sweet taste when eaten raw.
When used as an ingredient in cooking, they add flavor without adding too much heat. Green onions are also high in vitamin A and low in calories.
Green onions are most commonly served sliced raw on top of salads or tacos.
23. Leeks
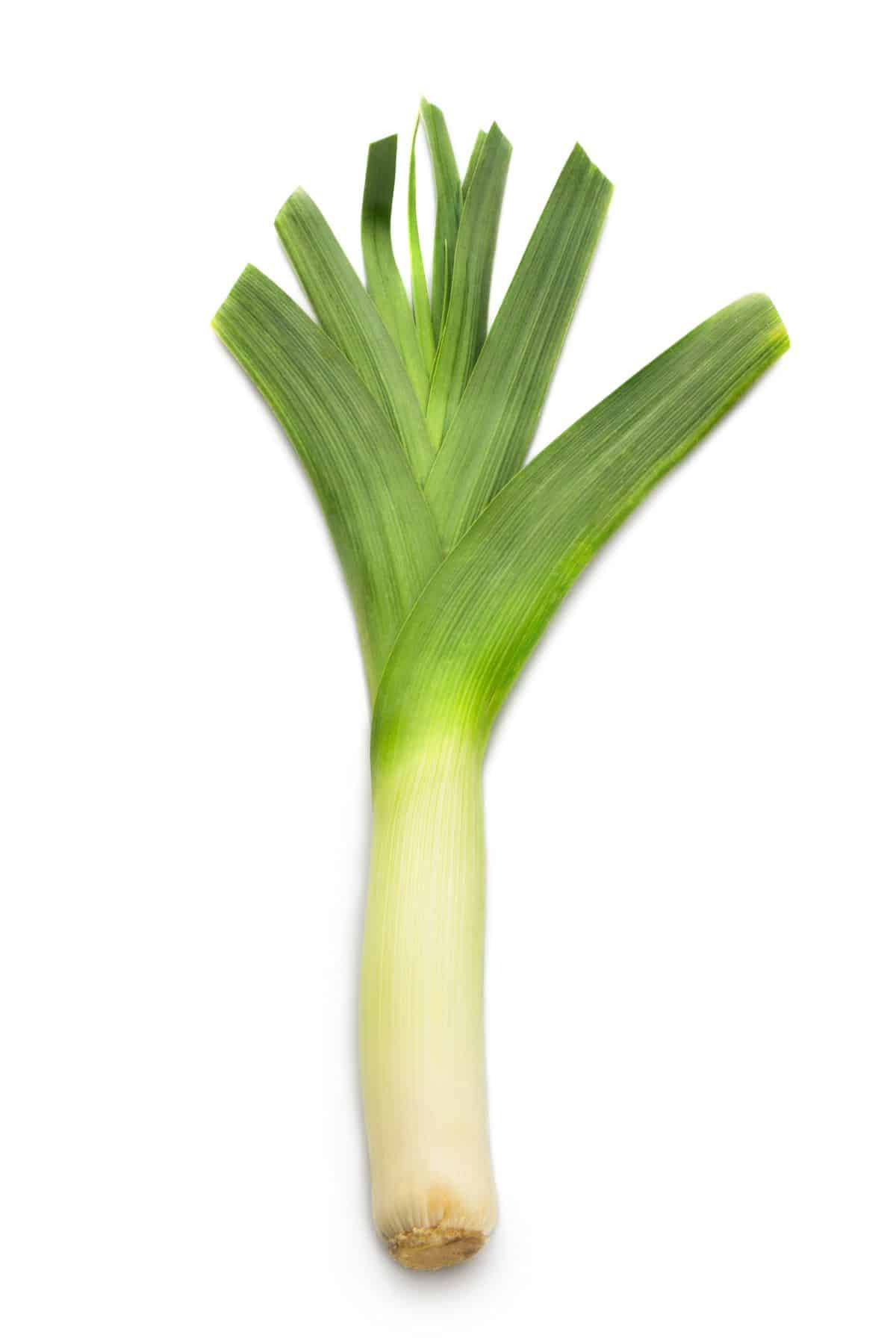

Leeks are vegetables that belong to the Allium family, closely related to onions, garlic, and shallots. They have a long, cylindrical white stem that transitions into green, flat, fan-like leaves.
While they resemble large scallions in appearance, leeks have a milder and more delicate flavor, often used to enhance soups, stews, and other dishes.
Additionally, leeks are a good source of dietary fiber, promoting digestive health and providing a feeling of fullness.
24. Artichokes
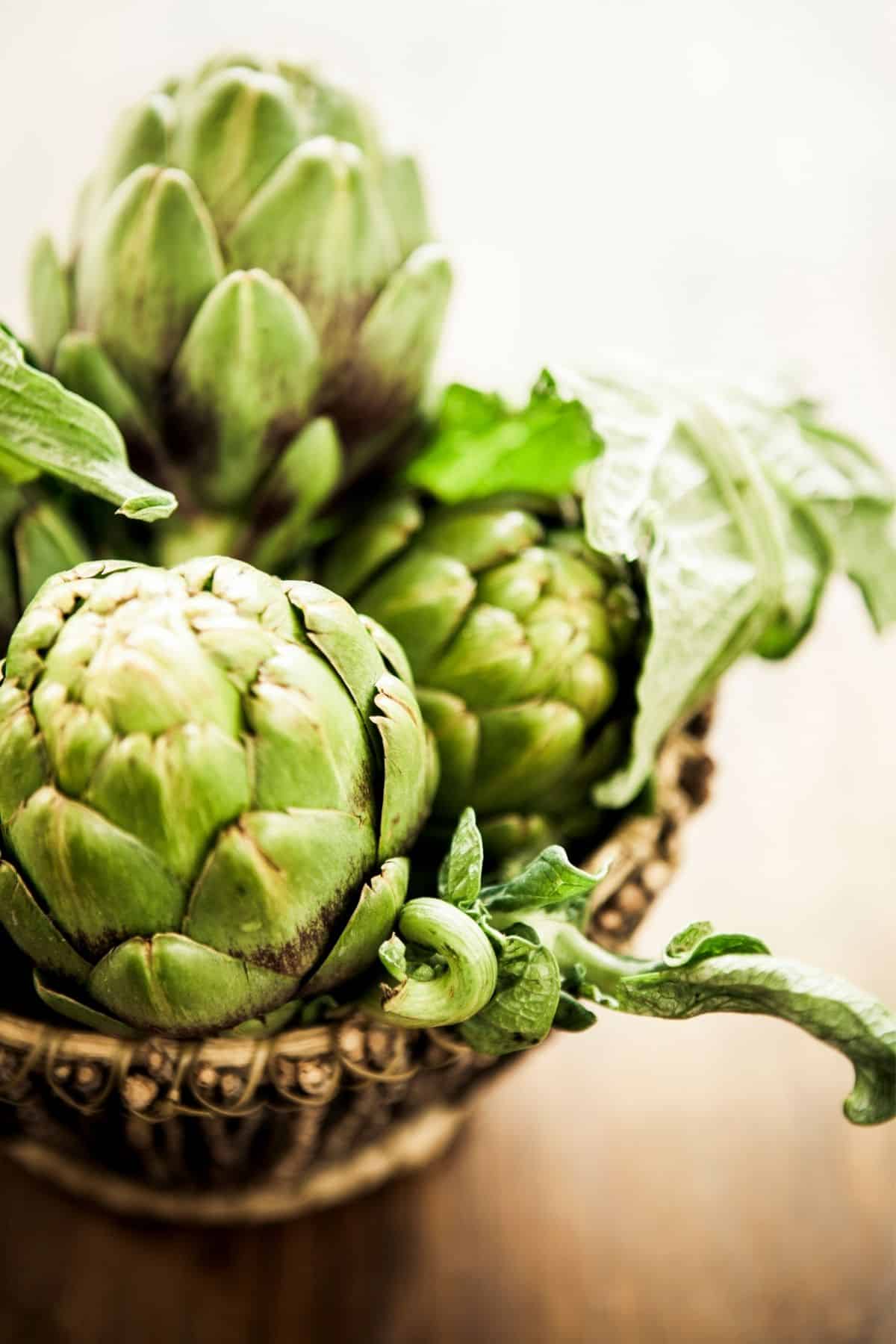

Artichokes are edible thistle plants native to the Mediterranean region. They have a unique appearance, characterized by their layered, green, petal-like leaves and a fleshy base known as the “heart.”
Typically, both the heart and the softer parts of the leaves are consumed, while the tougher leaves are discarded.
I love making Instant Pot Artichokes!
Artichokes are nutrient-dense, boasting a rich supply of fiber, vitamins, and minerals such as vitamin C, vitamin K, folate, and magnesium. They contain powerful antioxidants, notably cynarin and silymarin, which can support liver health and assist in lowering cholesterol.
25. Fennel
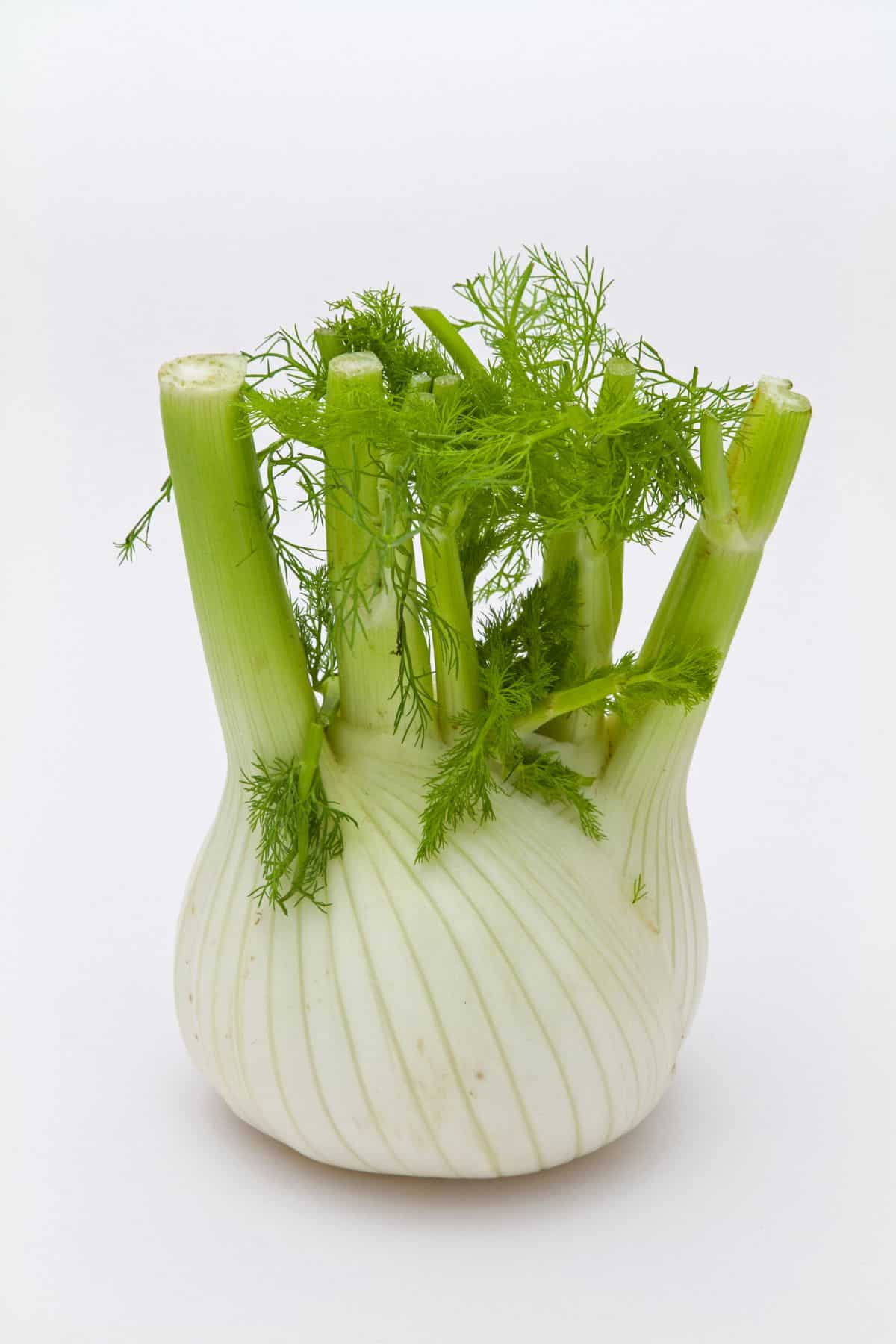

Fennel is a versatile vegetable with a distinct licorice-like flavor, native to the Mediterranean.
It consists of a bulbous base, stalks, feathery green leaves, and yellow flowers, all of which are edible. Its seeds are also used as a spice in various cuisines. I really like roasting fennel or adding it to soups and stews.
Fennel is packed with essential nutrients. It contains a unique combination of phytonutrients, including the flavonoid anethole, which has anti-inflammatory properties and has been linked to reducing the risk of certain cancers.
26. Endive
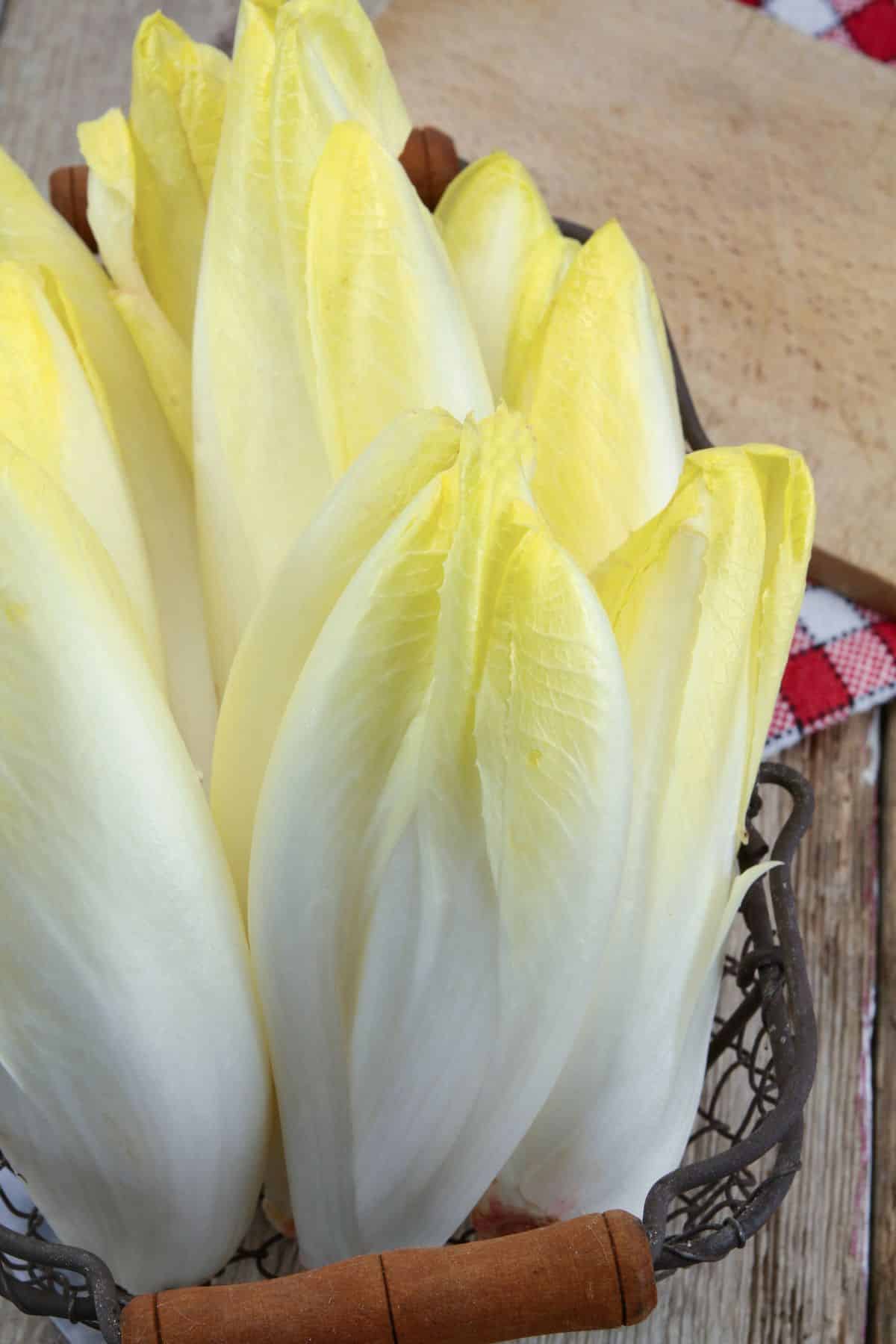

Endive is a leafy vegetable belonging to the chicory family, often used in salads and culinary dishes. Its leaves can range from tightly curled with a slightly bitter taste, known as curly endive or frisée, to broad and smooth as seen in the Belgian or French endive.
Endive is a low-calorie vegetable dense in essential nutrients, especially vitamins A, K, and folate.
The presence of kaempferol, a flavonoid antioxidant found in endive, has been associated with protective effects against chronic diseases and certain cancers.
Look for endive in grocery stores in the produce aisle with the other types of lettuce.
27. Broccoli rabe
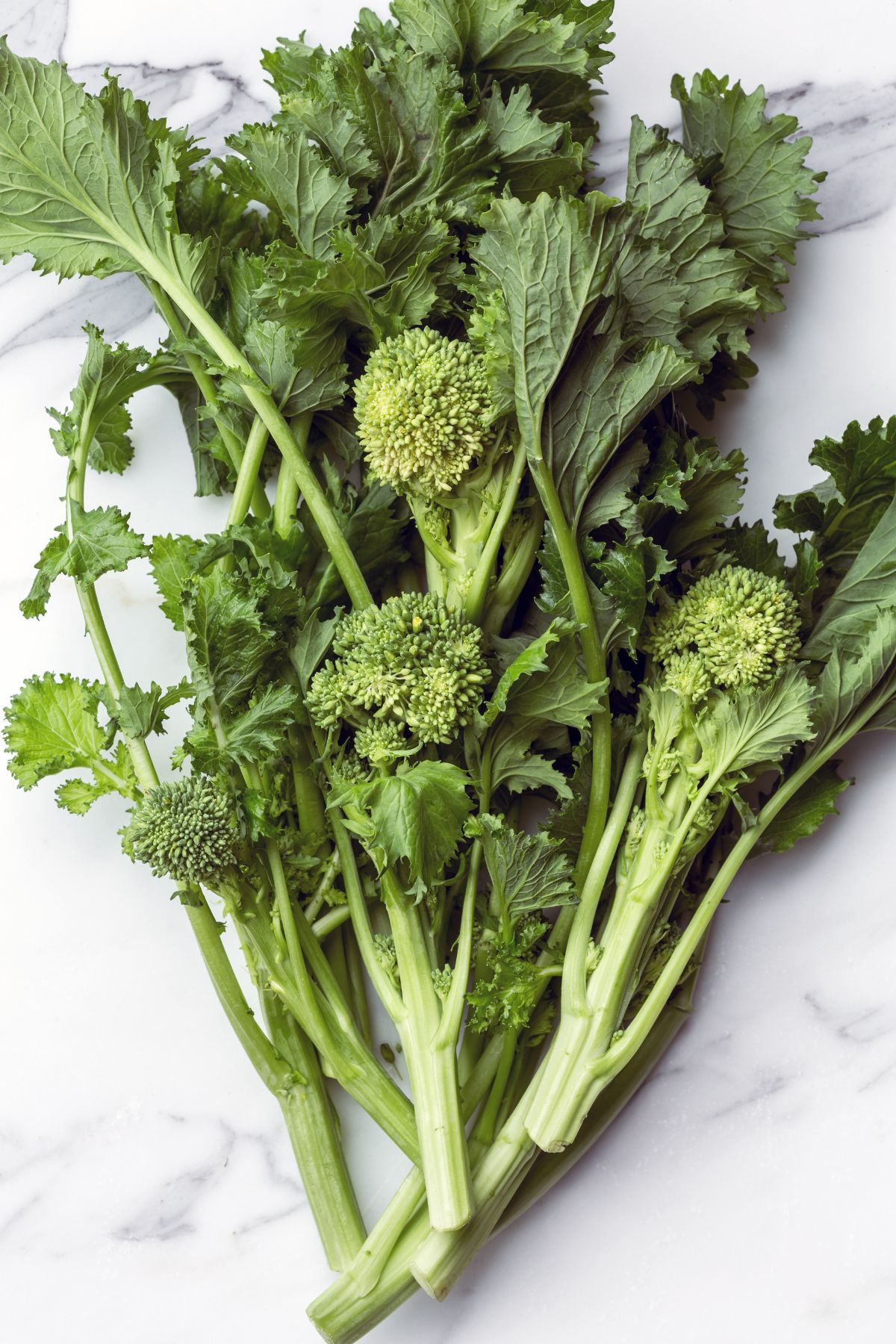

Broccoli rabe, also known as rapini, is a leafy green vegetable with small, broccoli-like buds and a slightly bitter taste.
Despite its name, it’s more closely related to turnips than to broccoli and is a staple in Italian and Chinese cuisines.
Broccoli rabe is a nutrient powerhouse, packed with vitamins A, C, and K, as well as minerals like calcium and iron. Its rich antioxidant content, especially glucosinolates, has been linked to potential cancer-preventive properties.
28. Peas
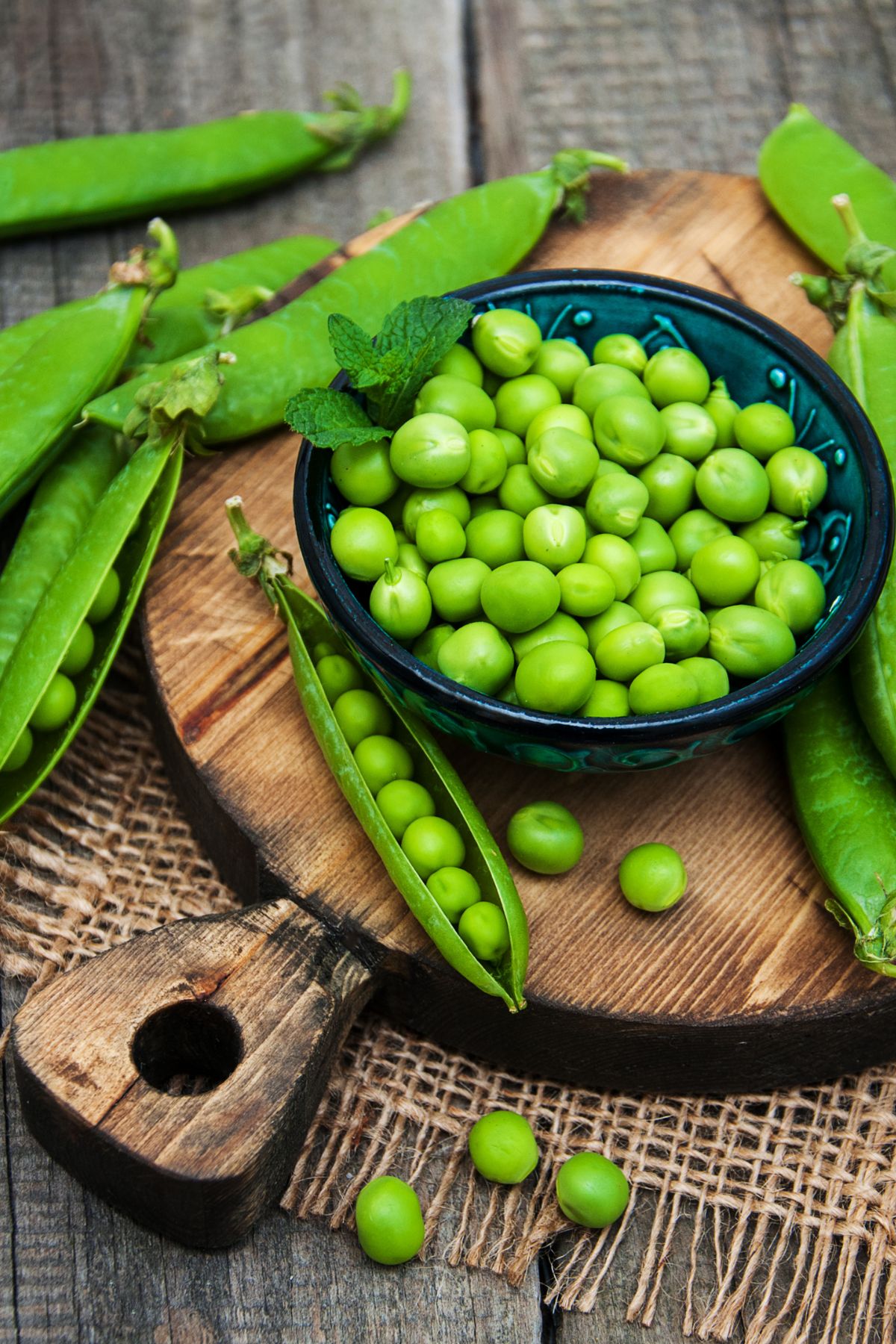

Green peas are small, spherical seeds that come from the pod of the Pisum sativum plant. A staple in many global cuisines, these legumes are typically vibrant green in color and have a sweet, starchy taste.
Green peas are rich in a variety of essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, C, and K, as well as iron and manganese.
They provide a good source of plant-based protein and are high in dietary fiber.
29. Romaine
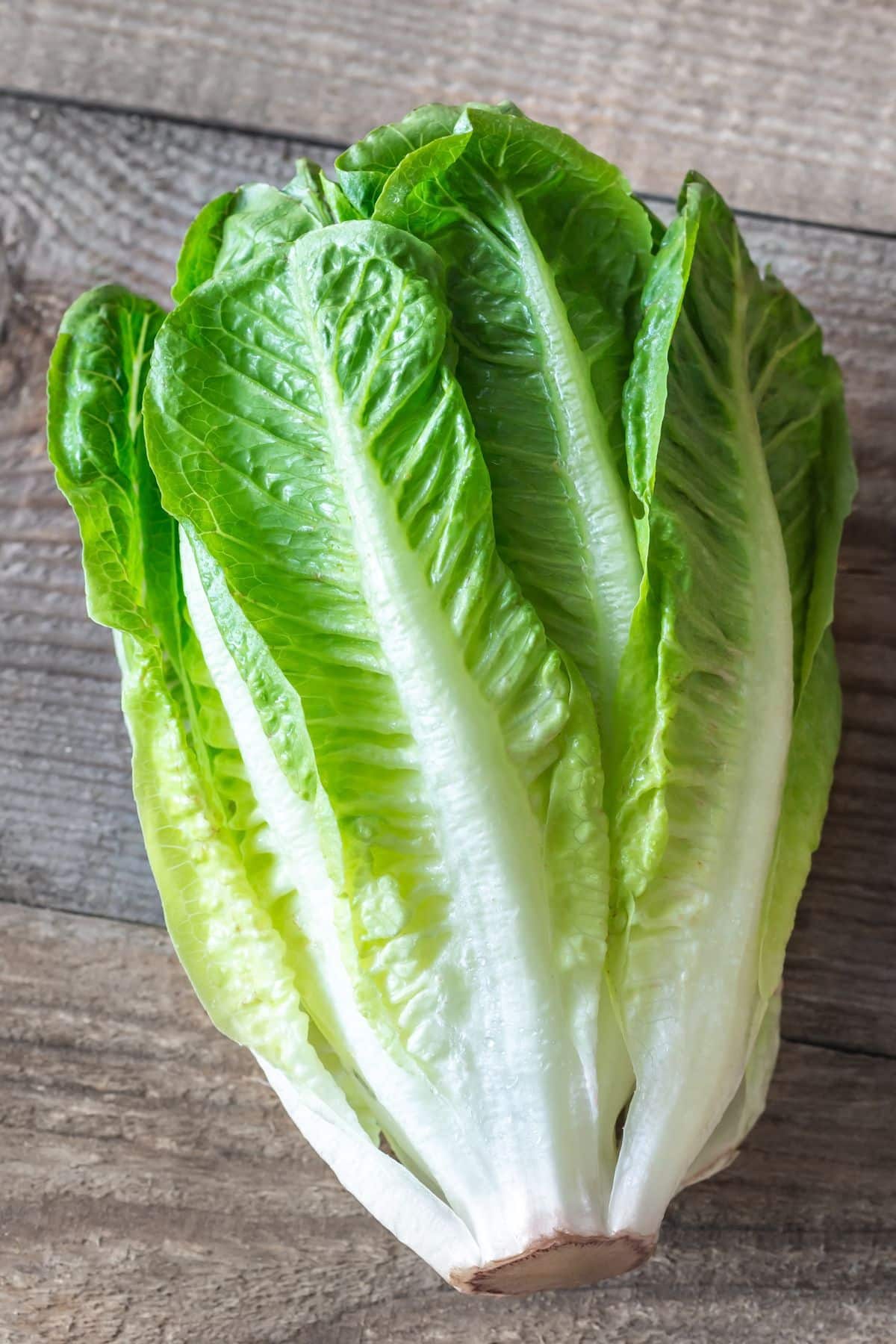

Romaine, often referred to as Cos lettuce, is a variety of lettuce known for its tall, elongated leaves with a firm rib down the center. Its leaves are crisp and have a slightly bitter and nutty flavor, making it a popular choice for Caesar salads and other culinary dishes.
I love using it in this simple romaine salad recipe.
Romaine lettuce is a hydrating and nutrient-rich vegetable, packed with vitamins A, C, and K, as well as folate.
30. Beet greens
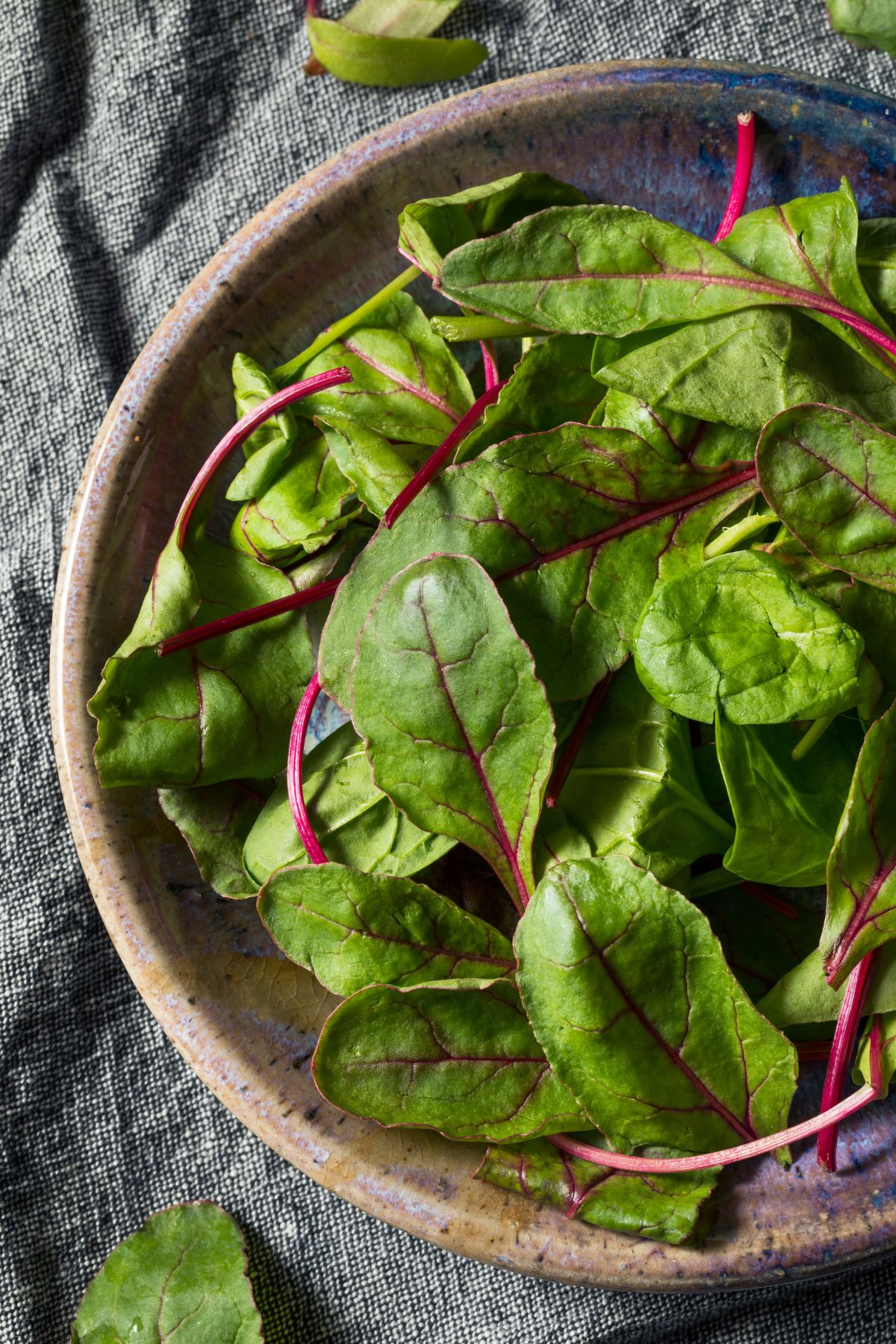

Beet greens are the leafy tops of the beetroot plant. Often overlooked in favor of the more popular root, these greens have a similar taste to Swiss chard with a slightly bitter undertone and can be eaten raw or cooked.
Beet greens are incredibly nutrient-dense, loaded with vitamins A, C, and K, as well as vital minerals like calcium, iron, and magnesium.
They contain potent antioxidants, including betalains, which have been linked to a range of health benefits such as anti-inflammatory effects and detoxification support.
31. Mustard greens
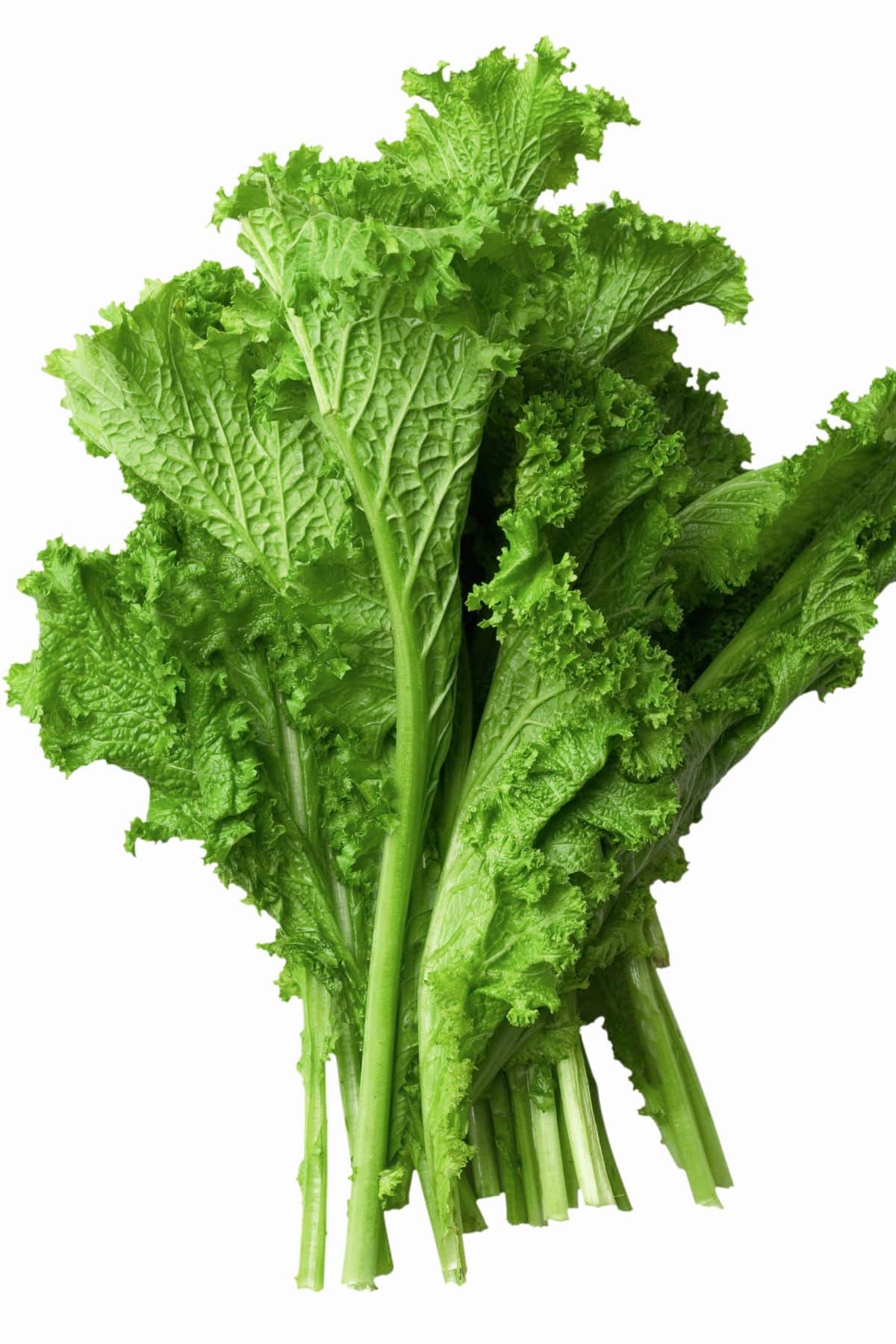

Mustard greens, stemming from the mustard plant, are peppery-tasting leafy vegetables frequently used in diverse cuisines, especially in Southern American and Asian dishes.
They have broad, wrinkled leaves that can vary in color from light green to dark purple, depending on the variety.
Mustard greens are packed with essential nutrients, notably vitamins A, C, and K, as well as phytonutrients like glucosinolates, which have antioxidant properties.
Bonus Green Vegetables
This list of the 31 Best Green Vegetables is not exhaustive! There are plenty more, but some tend to be more obscure and hard to find.
But, the next time you are at the grocery story, try looking around the fresh produce aisle and picking out some of the green-hued veggies that you’ve never had before.
Some other green veggies that you can try include baby lettuce, turnip greens, and romanesco cauliflower.
Health Benefits
Some reasons why green vegetables are so important to our health include:
- Phytonutrients: Dark green vegetables and leafy green vegetables contain special compounds that boost health.
- Vital Minerals: Most green veggies are rich in nutrients, vitamins, and minerals, not to mention antioxidants.
- Chlorophyll: This healthy compound gives them their distinct green color.
- Dietary Recommendations: The FDA suggests consuming 2-3 cups of vegetables daily to help us reach our minimum fiber and nutrient intakes.
- MTHFR Mutation Assistance: Green vegetables can assist with MTHFR mutation because they are rich in folate.
So, in order to get these amazing health benefits, I’ve put together this Green Vegetables List. Enjoy!
How to Eat More Green Vegetables
Green vegetables include any vegetable that’s green, of course! But different types of green vegetables belong to different families and provide you with different phytonutrients that have numerous health benefits.
Try adding one new green vegetable to your diet every week in order to get the most variety of antioxidants and health benefits.
For help with how to cook veggies, see my article on How to Cook Vegetables to Taste Good.
You may also like these lists of the Best Green Fruits or the Best Orange Vegetables!
Green Vegetable Sample Meal Plan
Green vegetables are versatile and can fit nicely into almost any meal. You can saute them, steam or boil them, roast them, or enjoy them raw or blended into a smoothie.
Here are some tips for cooking green vegetables for breakfast, lunch, or dinner:
- For breakfast, finely chop leafy greens like spinach or kale and saute before cooking into a scramble or frittata. Sprinkle with parsley or cilantro for extra nutrients.
- Another breakfast or snack option is a smoothie. Blend spinach, zucchini, cucumber, or mint into your smoothie. You won’t be able to taste the more neutral vegetables and they will add some fiber and nutrients. See my favorite Swiss Chard Smoothie.
- For lunch, throw together a big salad filled with lettuce, some dark leafy greens, and microgreens. Here’s a great kale salad recipe.
- For dinner, enjoy a side of roasted broccoli, okra, or asparagus. Roasting vegetables brings out a natural sweetness and adds a caramelized crunch. The air fryer comes in really handy when you want an easy green vegetable side dish. See all of my healthy air fryer recipes.
FAQs
A serving of green vegetables is roughly one cup. The FDA recommends 1-3 cups of vegetables per day for the average adult. However, it may be beneficial to consume more vegetables to ensure you’re meeting optimal dietary guidelines (not just minimal guidelines) and consuming enough fiber.
Vegetables, especially green vegetables, are low in calories and high in fiber and nutrients. You can eat plenty of veggies as part of a healthy diet, no matter your weight goals. Try to include vegetables with every meal, and include a variety of green vegetables in your rotation.
A serving of vegetables will depend on the vegetable. A serving of sweet potato is very different from a serving of spinach, calorically. A serving of leafy greens is usually one cup and a serving of other vegetables is usually listed as as half a cup, cooked or raw. Many recommendations include using “half your plate” as a guideline for veggies.
It’s possible! Green vegetables tend to be low in calories and carbohydrates, but very high in antioxidants and micronutrients. Try adding 1-3 servings of green vegetables to your diet and see if it helps you lose weight or manage your weight over time.
More Helpful Resources on Healthy Eating
Conclusions
For many reasons, it’s very important to eat at least several servings of vegetables a day, with an emphasis on green vegetables. You can make your life easier by incorporating a serving of veggies with each meal, from smoothies to salads to side dishes. Find preparation techniques that you like so you enjoy eating your vegetables.
Don’t forget to join my newsletter list to get exclusive clean eating recipes and tips. The newsletter is 100% free with no spam; unsubscribe anytime.
About the Author: Carrie Forrest has a master’s degree in public health with a specialty in nutrition and is a certified holistic nutritionist. She is a top wellness and food blogger with over 5 million annual visitors to her site. Carrie has an incredible story of recovery from chronic illness and is passionate about helping other women transform their health. Send her a message through her contact form.
Note: this post is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Please consult your healthcare provider for recommendations related to your individual situation.






















Carrie I was referred to a dermatologist by my primary care doctor. I don’t even know if we have The type of doctor you mentioned. I am in WV and I know we have regular dieticians and all but, I don’t know about the one you mentioned. Even though my body is responding favorably to the veganlike diet I will keep my appointment scheduled for August. I want to make sure that all is well. I just wanted to see if this is doable for me since my skin is clearing and all. I am doing all I can to not become dependent on harsh medication for the rest of my life. So I am just finding out about this as my primary care doctor has referred me. He would never venture to other types of medical practices.
I am just coming to you for ways to prepare meals as I progress in this. Don’t worry, I know you specialize in other areas So I don’t expect you to fix my issue just help me plan plant based meals.
Thank you once again for the reply Carrie.
Hi Sharon! I don’t specialize in plant-based meals, but all of my recipes are gluten-free and dairy-free. I hope you find my recipes helpful! I try to make them very allergy-friendly since everyone has different needs.
Hi Carrie,
The short of it is I have non diagnosed psoriatic arthritis. Appointment isn’t until August. I just started the 3 a day green smoothies and eating veggies to go with it. I had one this for 14 days and shooting for 30. So far my head stopped itching, my one lesion is flattening. My hand swelling is the same and my toenails look the same. I am trying my best to avoid meds. I have researched the web and some are too far into this for me to make good sense of this. Then I stumbled on to you. I believe God led me here.
So my vegetable will be broccoli and I may just eat it throw it into my smoothie. I want to eat vegetables without feelings of paranoia if I have chicken or fish after my 30 days. I want to slowly incorporate the good food back in. Sorry for the long story but I’m kind of lost but headed in the right direction and I believe you can help me. Thank you again,
Sharon
Hi Sharon, I don’t have a lot of experience with your condition, but I’m glad you are doing better! Are you going to see a functional medicine doctor? In my experience, they are the best at using food and supplements to help treat medical conditions.
I’m so thrilled to have found your site! I don’t know what links I clicked to end up here, but I’m excited to explore your knowledge and recipes. This is the first article I’ve read on your site, and the picture of the butterleaf lettuces has made my body feel like jumping in and snarfing them up. Butterleaf lettuce and okra are on the grocery list for this week. Thank you for setting up this website.
Awwww, thanks Debbie! I’m glad you found my site too! I’ve actually been blogging since 2009! 🙂
I love vegetables. Don’t eat them with every meal but I will give it more of a go.
Thanks, Jo! I’m thrilled to hear you love veggies!
Going to have roasted asparagus tomorrow for supper. Can’t wait unti we can plant our own garden in the yard but Michigan has been a little slow to let go of Winter this Spring.
Sounds great, Kathy! A garden sounds like a great idea this year!